
Follow this guide to create your own SMART goals for SEO to help demonstrate the impact of your optimization efforts to your employers or customers.
a goal is useful only when it is created.
, like many overused marketing terms and platitudes, “goal” can become a domineering or meaningless word or an aimless goal.
employers may hand them over to someone else without fully understanding the feasibility of completion. Employees may feel pressured to achieve the specified goals, whether realistic or unrealistic, without a plan on how to achieve them.
in particular, marketing leaders often ignore SEO’s goals and automatically work for them behind the scenes if they think organic products are a free access.
those who have worked in the SEO field, even for a short time, know that this is not the case.
, especially in enterprise organizations. While it is challenging for
to determine the full impact of a person’s SEO work, there are a variety of key performance indicators and effective methods to track the effectiveness of optimization. The most useful way for
to create meaningful goals is to apply the SMART framework to your key performance indicators.
you can apply the SMART framework to any goal, company, or business. But for SEO, there are some special considerations to include in the process of setting your goals. By layering SEO in the process,
will find that goals accurately reflect the impact of your SEO work and prove that you can achieve what you promise.
Hidden
?
SMART means specific, measurable, operational, realistic (or relevant) and timely (or time-limited).
when creating any goals, make sure these five aspects apply to your goals.
as part of the goal-setting process, ask yourself each of these questions:
- , what exactly are you going to measure?
- , do you have a way to measure key performance indicators?
- , can you have an operational impact on this KPI?
- , have the specific projects you want to improve changed realistically based on your actions? Is it relevant to your company’s goals?
- in what time frame do you estimate to show the impact of your efforts on KPI?
through these questions, only when you can determine the reasonable answer to each question, can you move on to the next question.
once you have answered each question, translate your findings into a clear statement. That’s it, you have it.
‘s five principles of applying SMART target processes to SEO
SMART can be applied to any business, company, or customer.
, however, when creating SMART goals specifically for SEO, here is how you should consider applying each goal to your goal-building process. The goal of
specific content
SMART is to demonstrate the impact of specific marketing efforts, or in this case, your search and site optimization.
ultimately, you need to prove that your optimization work improves the goals and goals of your business or customers.
therefore starts setting each SMART target by selecting a specific KPI.
limits each goal to one KPI, which helps to ensure the accuracy of the remaining four conditions of SMART. When choosing SEO’s KPI,
first checks to see if you can relate your SEO KPI to broader business goals and goals.
this way, you can prove how your search optimization supports your company or customer’s marketing conversion funnel.
in this funnel, these KPI usually start with the general impression on the SERP (search engine results page) and end with sales, purchases, or other financial transactions. SEO key performance indicator
in the whole marketing funnel of
Marketing funnel top (consciousness)
Total number of impressions of
- . Number of searches on page 1 of
- .
- comes from the click-through rate of search engines.
- comes from the click-through rate of search engines.
- comes from the user of the search.
- is the number of page views from the search. The page conversion rate of
- from search traffic.
- comes from revenue from search traffic.
Bottom of marketing funnel (conversion)
you may tend to rely on other SEO metrics, such as specific result types, including answer boxes (also known as feature segments), or locations where people also ask.
, however, there are two reasons to avoid these types of indicators.
they can fluctuate sharply in ways that have nothing to do with your efforts, and more importantly, they are not directly related to large business goals such as traffic and conversion rates.
, by contrast, the ranking on page 1 represents the number of times your content appears on page 1 of SERP. If your content is not on the first page, the chance of clicking is less than 2.5%.
so your presence on page 1 is a huge indicator of the organic traffic you might be able to drive.
similarly, conversion rates and revenue from search are particularly powerful KPI, which can be included in your goals because they help demonstrate the return on investment of SEO and content marketing, both of which are key determinants of marketing success.
overall, it is important to make sure that our goals are clear and relevant to our business goals, so that everyone from the board to the marketing department can understand what success looks like.
Fortunately for measurable
, as long as you have the right platform, tools, and / or software settings to ingest your data, most SEO metrics are easy to track:
- site analytics, traffic and access sources can be tracked through tools such as Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics or other tracking software. The
- search engine allows you to track the popularity, ranking, and keyword hits of your site through tools such as Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Platforms such as BridgeEdge, Conductor and Semrush can capture the ranking, ranking changes, keyword MSV, result types, and so on, of the keywords you track and the keywords you study. Some also integrate functions that allow you to ingest and crawl data from your website.
- site crawling can also be done through separate tools, such as ContentKing and DeepCrawl, which can track technical SEO components, such as title tags, meta-descriptions and alt tags, mark site errors, monitor core network indicators such as site speed, and so on.
before you can add any metrics from these sources, you need to establish a benchmark for it.
times and reports will be discussed in more detail when we discuss T in SMART, but basically, your goals need to be compared between two different time points.
in order to effectively compare data, you must establish a baseline for the previous month, if not a year. Unfortunately for
, it can be particularly difficult to prove that certain changes have led to specific measurable indicators of SEO. This needs to be clearly expressed when building and interpreting your goals.
, however, using market segments to track the specific pages you update and the keywords you are trying to optimize will help prove whether your optimized results have improved. By trying to make sure that you (or your content or web team) keep your optimizations as close as possible,
will make it easier for you to track changes over time.
achievable and achievable
has many implementable and actionable ways to affect organic search performance.
search engine optimization initiatives include keyword research, competition analysis, website audit, and data analysis to provide optimization recommendations for new content, existing content and technical fixes, and improve conversion funnels.
doesn’t want to help you beat your competitors.
however, not all SEO work can be tracked or explicitly measured. Some challenges include not knowing when
- Google crawls a new page or re-crawls an optimized page. When
- SERP is updated to display optimized content.
- if the content at that time is still relevant to consumers to encourage clicks.
- if there is any damage on your site that leads to errors or damage to rankings or Core Web Vitals. The last one in
represents why website health, internal / external links, or other technical SEO indicators are not recommended for SMART goals. There are too many variables you can’t control.
, however, by building your SMART goals in a way that follows the conversion funnel, you can see the whole picture and should highlight the organic success trend more clearly.
if any part of the funnel fluctuates unexpectedly, this may help identify external problems that have a negative impact on your success.
in addition, as long as you plan your optimization in advance, you can adjust your monthly goals according to the impact of your plan.
as long as you make these updates, you can know what you can achieve within a month after each round of updates is launched.
even if you don’t set SMART goals for all parts of the funnel, tracking them will still help you better understand the role of organic matter at each stage and help you develop your goals. The realizable
of
also means realistic. No matter what the leadership expectations are, and whether you want to set positive goals or not, you need to set reasonable expectations.
, a start-up company or a company with very low SEO maturity, may set steep goals, at least initially, if they plan to implement improvements based on the basic principles and foundations of SEO.
if a company has optimized its technical components, they are often monitored and the content is often optimized, then their SEO maturity is already quite high. It may only grow by 7% 12% year-on-year on indicators such as organic flow.
therefore, the company background is the key. Before
chooses specific indicators and estimates the improvements you will make, ask yourself:
- , can you make real progress on the keywords you pursue? Does
- have any practical interest in the page you are trying to optimize?
- , will your optimization work really take place?
- do you have enough resources to do the necessary SEO research and release changes?
- , have you set up a report to measure your KPI?
- does the expected impact you intend to have on SEO match the SEO maturity of the company or customer you are optimizing? When
creates SMART targets, any one of them should be considered a hindrance. Some versions of
use correlation as an R.
, however, including the specific KPI in the conversion funnel, consistent with broader business goals and objectives-all of which have been established in the process-will ensure relevance.
has time limits and scheduling
results should be proved within a specified time frame.
creates a schedule with start and end dates to track when you expect to see the results you want based on when you start working.
this motivates you to achieve your goals within a specified period of time and to proactively manage the expectations of your leaders and colleagues when you are asked to speed up your efforts or ask why you didn’t achieve any goals early.
The actual optimizations you want to measure, whether content or technology, can often be calculated immediately after launch, especially when SEO experts can edit the site directly.
, however, in order to fully measure the impact of SEO work and prove its effectiveness, whether it’s content or technology, you usually have to wait at least a month before you can start measuring meaningful results.
as long as search engines crawl changed pages, their impact can be seen.
but their impact will take at least a month to take into account the delay in fetching, let the changes be reflected in SERP, and give users access to content.
, especially if you have a site that is not crawled very often, it may take a long time for Google to re-crawl your site and make it aware of this change. Considerations for
SEO SMART goals
once you have considered all the above five components, please carefully consider how they apply to the work you do on a regular basis.
if you find that your project does not allow you to set such goals, it may be time to reconsider your efforts or communicate with your manager about expectations, available resources, and tracking options.
Framework for creating SMART SEO goals
to start building your own SMART SEO goals, apply this process to each goal:
- Pick any of the key performance indicators. One at a time.
- ensures that it is in line with broader business goals.
- Review all SMART concepts and confirm that you can use the following matrix to apply this principle to your work.
SEO SMART Target Matrix
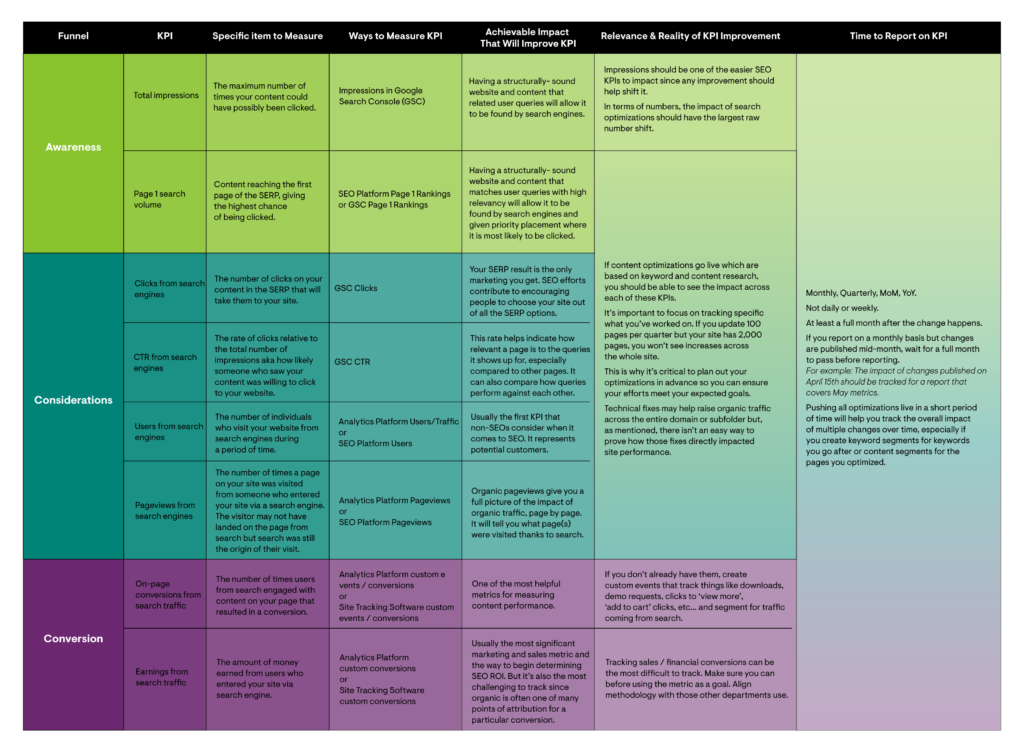
View and download the above target matrix table
The example
of
SEO SMART goals is based on this framework, and you may create SEO SMART goals, such as:
- will move 20 optimized pages currently on page 2 to page 1 between the second quarter of 2023 and the third quarter of 2023.
- will increase monthly hits from Google by 6 per cent (May to June 2023).
- will increase your site’s organic traffic by + 10% by August 2023.
- maintains a base of 20000 organic visitors a week.
- will increase the organic traffic of optimized pages by + 16% within two months after optimization (July 2023). Organic downloads per page increased by 7 per cent between new content released by
- in the first half of 23 and new content released in the second half of 2022.
- revenue from organic sources will increase by 5 per cent over the next three months (June-August 2023).
customizes your SMART goals for SEO
although you can adjust these goals to suit your SEO goals and any business, but you still need to consider the customizations you need.
when working on part R of your SMART goal, make sure that the percentage you will increase is consistent with the level of effort you can achieve.
is based on the impression of each optimized page, the original level of organic users and conversion rates, and the increase in the original location of the total MSV and keywords.
if you have time, test the impact of your optimization for a month or two to determine the type of ascension you see and aim to replicate it. No matter how
is customized, make sure your process follows the core terms of SMART, as summarized in this infographic:

How to set SMART SEO goals
The challenges
faces when creating SEO SMART goals
in some cases, you may need to expand your goals to get approval.
although you may not have a choice on this issue, tell the leader that your estimate is based on the impact you think you will have on your optimized pages and keywords. Some technical improvements in
, improvements in structure and speed, and optimizations that affect more parts of the site (headers, footers, pages with multiple incoming and outgoing links, etc.) may contribute to overall searchability.
however, they are rather difficult to attribute to specific actions and are particularly challenging for reporting.
insists on reporting on your more traceable efforts.
Summary: setting goals for
is a challenging process.
this is a serious task that requires careful consideration, teamwork and, most notably, the ability to provide the necessary conditions for achieving your goals.
and just because you create a goal using the SMART process doesn’t mean you can always achieve it, let alone surpass it.
, however, the SMART framework-if applied carefully, accurately and honestly, will eventually help you help yourself.
will support your ability to prove your value when implementing SEO and demonstrate how you and your efforts benefit your company and its goals.

