Google’s web crawlers are constantly searching the Internet for new and updated pages.
when these crawlers index the content of a site, they don’t just use that information to provide search results. They back up the pages and add them to the consolidated database called Google Cache.
you may have used the Google cache to view older versions of Web sites that are closed or is not loaded correctly. But did you know that you can also use it to solve problems on your website? It can even help you with your SEO work.
this article introduces Google Cache and its checking methods. We’ll also learn how Google caching can help-and when you shouldn’t rely too much on it.
- what is Google caching?
- Why Google caching is important how
- looks at Google caching
- uses Google caching reasons
- Google caching restrictions why
- can’t find cached web pages? How does
- solve the problem of caching pages on a website? how does
- remove pages from the Google cache?
Google cache page is the original HTML backup of the page content obtained during the Google crawl. Google cache as a whole consists of these backup pages.
if you look at the cached version of the site, it may look a lot like what the site looked like when it was crawled. But there are several reasons why things can sometimes be different from what you expect. The two main reasons for
are that
web pages are rendered by your browser, not by Google. This may result in differences from the current version of the site.
- JavaScript is not saved to the cache, so some parts of your site may be lost.
- is at the top of the cache page, and you will see a banner showing three things:
Cache the URL of the page-this is usually the URL you want to access. In some cases, such as a redirected URL, it will be different.
- Date on which this version of the page is cached-you can see whether the cache page you are viewing was created yesterday or last week. This may not be the last time you crawl your web page; we’ll talk about it later.
- Version-you can choose to view the full version, the plain text version, or the page source. The full version shows you the page rendered by the browser. The plain text version has turned off CSS and does not display images, but you will still see hyperlinks. Clicking View Source Code displays the source code of the page: the cached version of the
- home page example
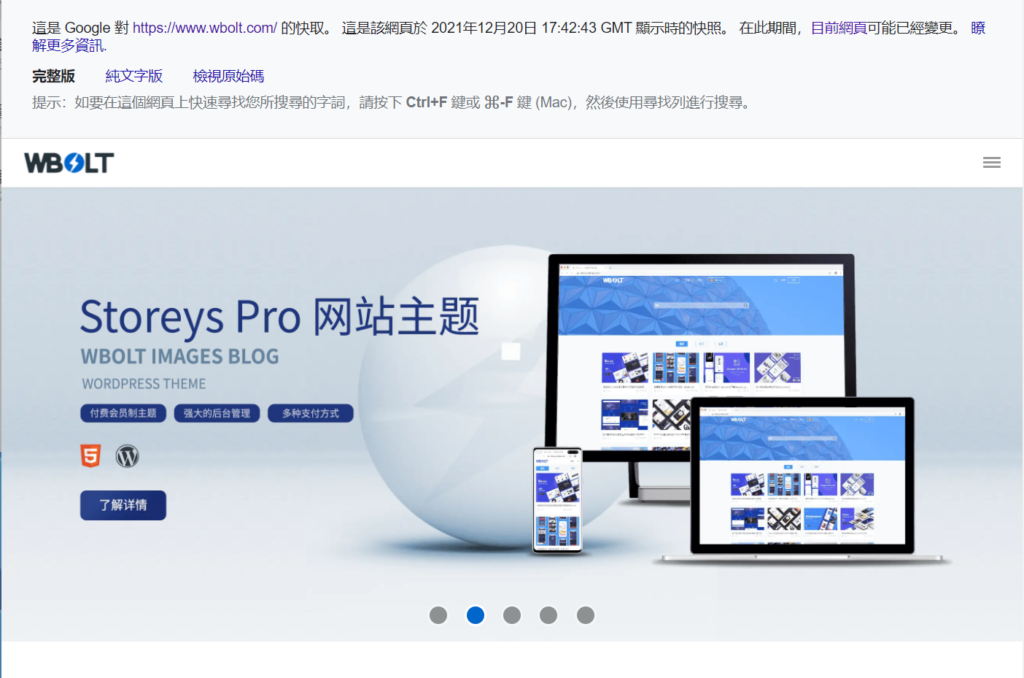
Why Google caching is important the main purpose of
Google Cache is for people to browse the Internet. It allows them to view pages that are closed or loaded with problems. There are other reasons why Google caching is important for
as the owner of the site. You hope your site never shuts down or breaks down, but it does happen. Having a cache allows users to use your content, even if some content does not work properly.
you can also use the cached version of your site to understand how your site is indexed and diagnose problems. Please continue to read for more information. How
views the Google cache
how you access cached Google pages from Google search engine results depends on the type of device you are using. In the desktop Web browser, you have two choices:
you can click the link to the cached version of the page in the Google search results.
- can go directly to the page.
- on mobile browsers, you can only choose to use direct URL.
View cached pages from Google search results
even if you have experience viewing cached sites from search results pages, you may want to read this article, because Google changed the way it looks for cached links in early 2021.
first, search Google for the page you want to view. Next to the URL on the page in the search results, you should see a drop-down triangle icon. Click on them and a pop-up window appears labeled “Page inventory”:
Google’s “Page inventory” feature
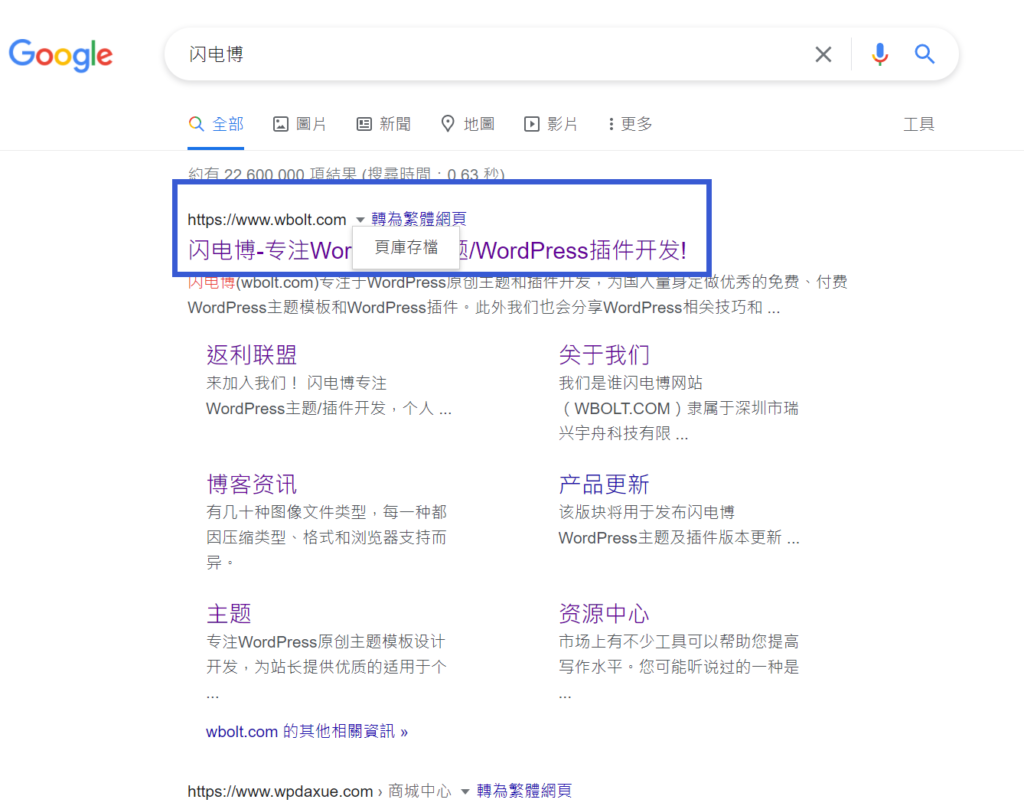
this feature is currently in the testing phase. It is designed to give you more information about the site (such as whether it is secure) before you click.
in some cases, you may not see the page inventory button. This may mean that the page is not cached; we will discuss what this means later.
however, if you are using a mobile device, you will not see any page buttons. In this case, read on for other ways to view cached pages.
modify URL View cached Page
for this method, you must know the URL of the page you want to view. Just go to the
search bar.
for example,
will take you directly to our cached home page.cache:website.xyzView other Google cached tools
you don’t need any special tools to view cached pages; Google itself makes it very easy. But there are some tools that have features that you might like.cache:www.wbolt.comChrome’s Web Cache Viewer extension allows you to right-click any link to view the Google cached version and Wayback Machine Web archived version of the page.
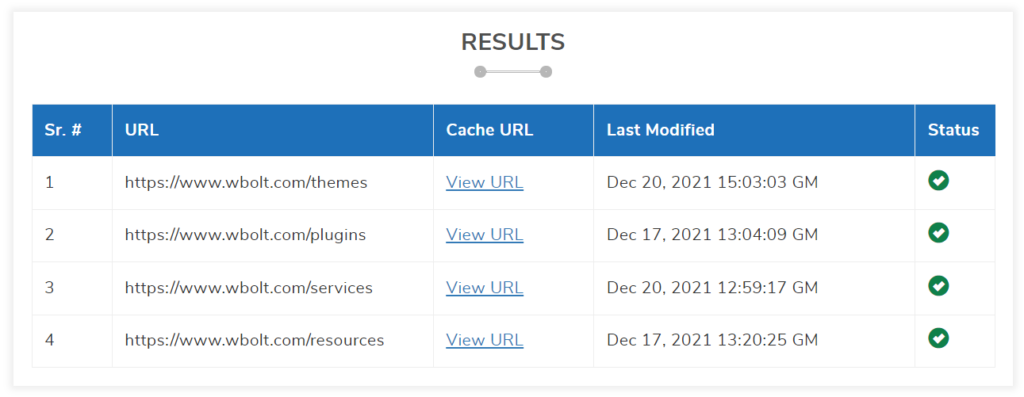
Google Cache Checker from Small SEO Tools allows you to view the cached URL and dates of up to five pages at a time:
Google Cache Checker
uses the Google cache to view the old version of the page
your page says it was cached yesterday, but you want to see last week’s version. Is Google caching okay?
, I’m sorry. No.
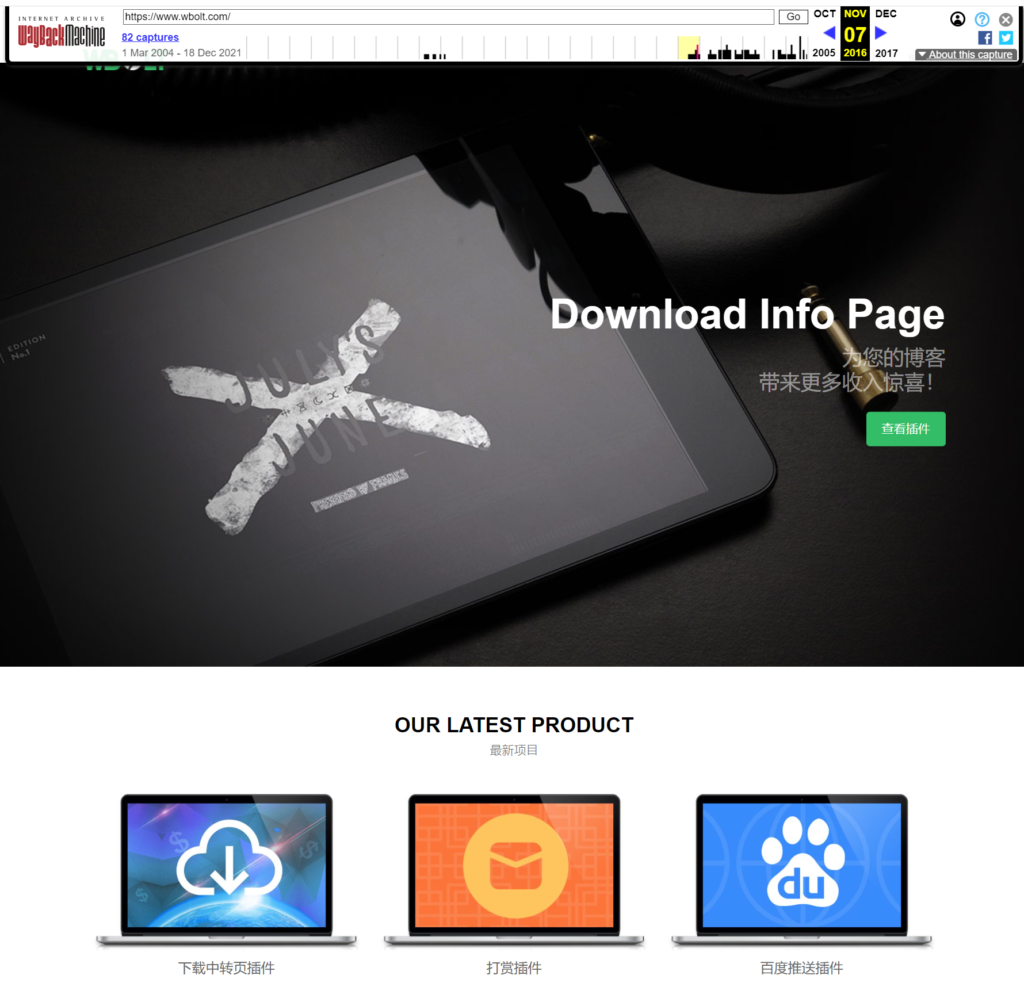
Google can only show you one version of the cached page. To view previous versions of the site, you can use tools such as Wayback Machine, which is an archive of past web versions.
, look what we used to look like! 2016 website on
Wayback Machine. The reason
uses Google caching is the fact that there are other tools that can be used to do all of the following– in many cases, more complex tools.
but Google cache is difficult to match because it is fast and easy to check. This makes it a valuable way to monitor some aspects of a web page.
as the site owner, you can use Google caching in the following five ways.
1. Check for duplicate content
sometimes you click on the cached link and go to a different page than you expected. One of the reasons for this in
is repetitive content. When Google sees two pages that are highly similar, it may decide not to separate them in the index. This results in only one being saved in the cache.
Google caches multiple pages under the same link to remind you that there is duplicate content on your site. Repetitive content can not only cause a confusing caching situation– it’s bad for SEO.
, please take this opportunity to examine the two pages and find a way to distinguish them.
2. Verify that Google complies with your specification label
maybe the duplicate content on your site is intentional, but you have added a
tag to tell Google which version to crawl.
checks the cached version of Google for one of the pages you don’t want to crawl. You should be taken to the cache of the canonical page.
3. Make sure that your marketing efforts have been grabbed
you have stepped up your SEO or content production efforts, and you want to make sure that Google is indexing these changes. The cached version of therel=canonicalQuick View page tells you that it has been crawled.
, note that if your changes do not appear on the cache page, they may still be indexed. If you are worried, you can go to the URL Inspector of Google Search Console to confirm. However, if you see your updates in the cache, you know that they have been indexed and will begin to affect your search results rankings.
4. Keep a close eye on changes on competitor sites
when competitors suddenly occupy your position, you will mind your own business and enjoy your position at the top of keyword search results. What did they do to get there? You can use the Google cache to find it. Compare their cache page with the current version-you will be able to see recent changes made by competitors.
5. To retrieve the latest version of your website
you should always back up your website, just in case. In other words, sometimes the worst happens, even the most prepared.
although the Google cached version of your site does not replace full backups, it does sometimes allow you to see what the page looks like before a disaster occurs. You can use it to retrieve lost old content or code. The limitations of
Google caching
Google caches can provide useful information, and if anything seems strange, it may be worth investigating. But Google caching has some known limitations.
Google Cache won’t tell you when your page was last crawled
lets start with one of the biggest misunderstandings.
many people think that the cache is updated every time Googlebot crawls a page. Many other articles on this topic will tell you to use caching to see how often your page is crawled.
, this is not true.
we know, because Google’s John Mueller told us personally in the help topic:
generally, we don’t always update the cached page every time the page is crawled. Especially when there is no significant change in the page, we may choose to keep only the old date on the original text.
this is a professional tip: if you are looking for information about how often Google crawls your site, why, and which roaming devices you use, forget caching. The data is located on Google Search Console. You can find the crawl report under Settings in the sidebar.
however, you can only view this information at the domain level. Search Console won’t tell you how often each page is crawled.
pages may not render
correctly. Fortunately, some progress has been made in this area. Google’s Web Rendering Service is used to render real-time pages on Web, which was once based on an outdated version of Chrome. As a result, the latest browsers sometimes render cached pages differently from the current page rendered by Google.
Google Web Rendering Service has been using the latest version of Chrome since 2019.
however, if your version of Chrome is older, or if you are using another browser, the cached page may not render correctly. Another rendering problem with
is related to a lack of resources. The code backed up by Google may reference resources such as CSS or JavaScript. If these resources no longer exist or have been changed, the page will not render correctly.
Display error pages
We have studied how duplicate content or incorrect specification tags can cause the Google cache to display the wrong pages. As you might imagine, this limits the use of viewing a specific web page cache. It may come as a surprise that some pages of
are not cached with
, but it turns out that many pages are not cached at all. A common misconception of
is that an uncached site means that Google doesn’t think it’s essential, but it’s not necessarily true. Next, we’ll look at some of the reasons why the page may not be cached.
Why can’t I find the cached web page?
not all crawled pages are cached. If your page does not have a cached version, please do not panic! This does not mean that your page has not been indexed. The
404 error indicates that the page does not have a cached version of
. If you are worried that it is indeed not indexed, you can use Google Search Console’s URL Inspector to check.
to prove that indexed pages are not always cached, let’s go back to Google’s John Muller. On Twitter, he answered a user’s question about uncached pages:

, we don’t cache all the pages we index, so this could happen. Sometimes it takes a while, and sometimes we don’t cache it at all.
when users asked him if uncached sites were always of low quality, he said:
it can be a page of all sorts of strange technical quirks. The cache is a bit independent, so it doesn’t represent what we index and rank.
in other words, cached pages are not a ranking factor. Even if your page does not have a cached version, you can put it at the top of the search results.
but uncached pages are still worth studying. You can explore several different possibilities.
your page is JavaScript-based
, Google can index some JavaScript-based pages more easily than other web pages. But many JavaScript pages end up without caching or even indexing.
this is because most HTML is not loaded until the JavaScript is executed. If there is no indexable content, Google will not create a cached page. The
meta tag prevents caching
in your web page’s HTML code meta tag
means that the page cannot be indexed by Google, and
will block Google cache to block it. Any one of them will cause the page not to be cached by Google.
, maybe that’s what you want. But if you don’t realize that there is a
tag on the page, deleting it can solve your cache loss problem.noindexthis page is repetitive (or Google thinks it is)noarchiveif Google determines that your two pages are duplicated, please find a way to make them unique. Consider the different search intentions of each page. How
solves the problem of caching pages on a websitenoindexornoarchiveyour pages don’t have to be cached, but if you want to implement it, you can do something.
submits your page to Google
. If you are worried that Google has not indexed your page at all, you can check Google Search Console.
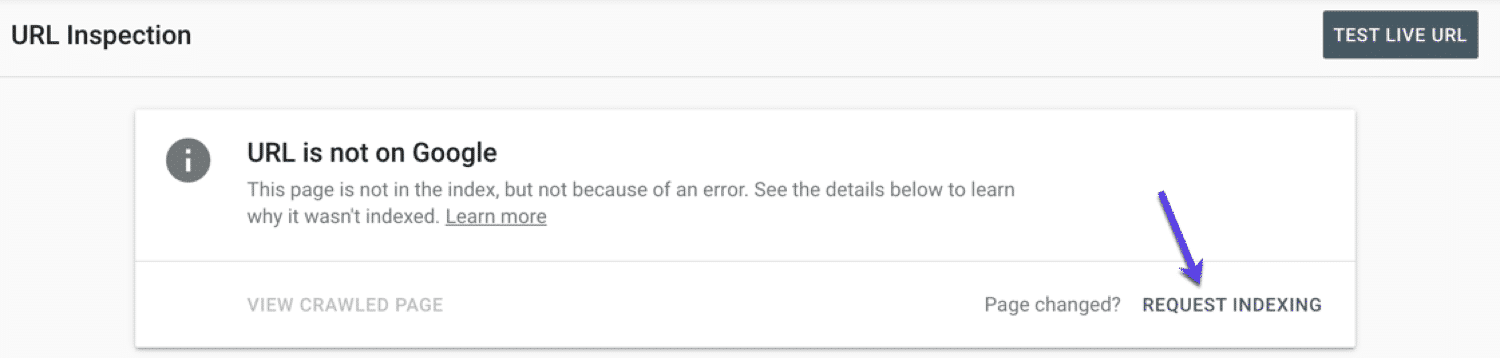
enters the URL of the page in the URL check search bar at the top of the Search Console. If it is the result of “URL is on Google”, the page has been indexed. If the page has changed recently and you don’t think Google has indexed the new version, you can click request indexing and ask Google to re-index it.
you may also get the result of “Page is not on Google”. If you do so, scroll down and you will be able to see some details about the page. For example, you can check whether the page allows crawling and whether the specification selected by the user matches the specification selected by Google. To request an index, click request Index:
Google Search Console-URL Index request
if you want your website page URL to actively submit to Google Search Console and request indexing, you can install the search push plug-in.
check for common site problems
We have covered several reasons why your page may not be cached, such as a lot of JavaScript and duplicate content.
beyond that, the best way to encourage frequent indexing is to create a high-quality site. Make sure you have optimized your site for mobile devices and that your site is fast.
if your page load time is too slow, it can even slow down the roaming speed of Google, resulting in index latency. How
removes the page
from the Google cache We think the Google cache is very useful, but for a variety of reasons, you may not want to store older versions of Web pages on Google’s server. For example, you may not want the page of the discontinued product to be available. One way for
to prevent page caching is to use the
and
tags mentioned above. If you want to keep pages but never want them to be cached, these tags are the ideal permanent solution.
you can also directly ask Google to remove the URL from the Google cache. To do this, go to the Google search console and click remove from the sidebar. Then click New requirements. At this point, you have two options: temporarily delete the URL and clear the cached URL. The temporary deletion of
means that the URL will not appear in Google search results for about six months. The cache will also disappear. The page will be re-indexed and re-cached when it comes online again (if you don’t want this to happen, you must add meta tags).noindexclears the cached URL exactly what it sounds like. The cache is removed, but the page is cached again when the site is crawled.noarchiveThis is a good way to do this if you want the old version of the update page to disappear. You can also push Google to update the cache of pages by submitting the page for indexing after the page has been changed.
summary
Google cache is not everything in the rumor. You can’t use it to check the last time your site was crawled-owning it won’t improve your search engine rankings. Sometimes, the version of the website it stores is strange, incomplete, or completely wrong.
but Google caching is useful for website owners. This is a quick way to check how your site is indexed, and it can help you identify and diagnose problems. You can also use Google Search Console to improve your search engine rankings.
如果您希望更新页面的旧版本消失,这是一个很好的方法。您还可以通过在更改页面后提交用于索引的页面来推动Google更新页面的缓存。
小结
谷歌缓存并不是传闻中的一切。你不能用它来检查你的网站上次被抓取的时间——拥有它不会提高你的搜索引擎排名。有时,它存储的网站版本很奇怪、不完整或完全错误。
但谷歌缓存对网站所有者有其用处。这是检查您的网站是如何编入索引的一种快速方法,它可以帮助您发现和诊断问题。您还可以使用Google Search Console来提高您的搜索引擎排名。

