Managing a website is a very challenging task. This is not always because of the difficulty of the task, but because of the number of tasks.
in addition to publishing site content, you must also update plug-ins and WordPress cores, remove spam comments, add internal links, and so on, and update them regularly.
although all of these tasks may seem trivial, you still need to browse the WordPress administration background to perform these tasks.
, that’s the problem. If you are reading this page, you may be facing the same problem: the WordPress administration panel is slow.
in this guide, we will explore what causes the WordPress administration background to slow down and how to speed it up.
Why is your WordPress background running slow? The slow management of
WordPress has a lot to do with the gap between supply and demand. The demand for out-of-the-box WordPress is so small that even basic shared hosting plans can be met. However, when you configure and customize your site, the demand may outweigh the supply, causing the WordPress administration background to slow down.
Let’s take a look at the common problem behind the slow speed of the WordPress dashboard:
- Too many plug-ins: while plug-ins can help you add different functions to WordPress management, some plug-ins can take up more memory than the host infrastructure can handle. For example, it is not a good idea to install a page generator plug-in on a basic shared virtual host plan.
- Outdated infrastructure: if you want excellent performance, older versions of WordPress and PHP are not the best choice. In addition, modern plug-ins usually adjust to the latest core versions of PHP and WordPress, so if you continue to use the old version, your WordPress hypervisor may run slowly.
- Bad host choice: you can’t install the Elden Ring game on the Pentium III and expect it to run. Similarly, it is not feasible to host a high-traffic commercial website on a basic shared hosting plan. You need a better hosting infrastructure to support huge traffic and a large number of concurrent login users. How
optimizes the running speed of WordPress management background
based on the above reasons and summing up past experience, let’s take a look at 13 tips that can help you improve the running speed of WordPress management background:
1. The front end of the newer PHP version of the
WordPress website relies on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, while the back end is almost entirely PHP. For example, the core and plug-ins of WordPress are usually written in PHP. If you are using a traditional WordPress theme, then your theme also depends on PHP.
, like WordPress, PHP is evolving year by year and has brought some security and performance improvements. This is one of the reasons why WordPress 2.0 requires PHP 4.2 or later, while WordPress 6.2 recommends PHP 7.4 or later.
you can check the PHP version of the WordPress site by navigating to tools & gt; site Health & gt; Information and then expanding the server in the WordPress panel. Does
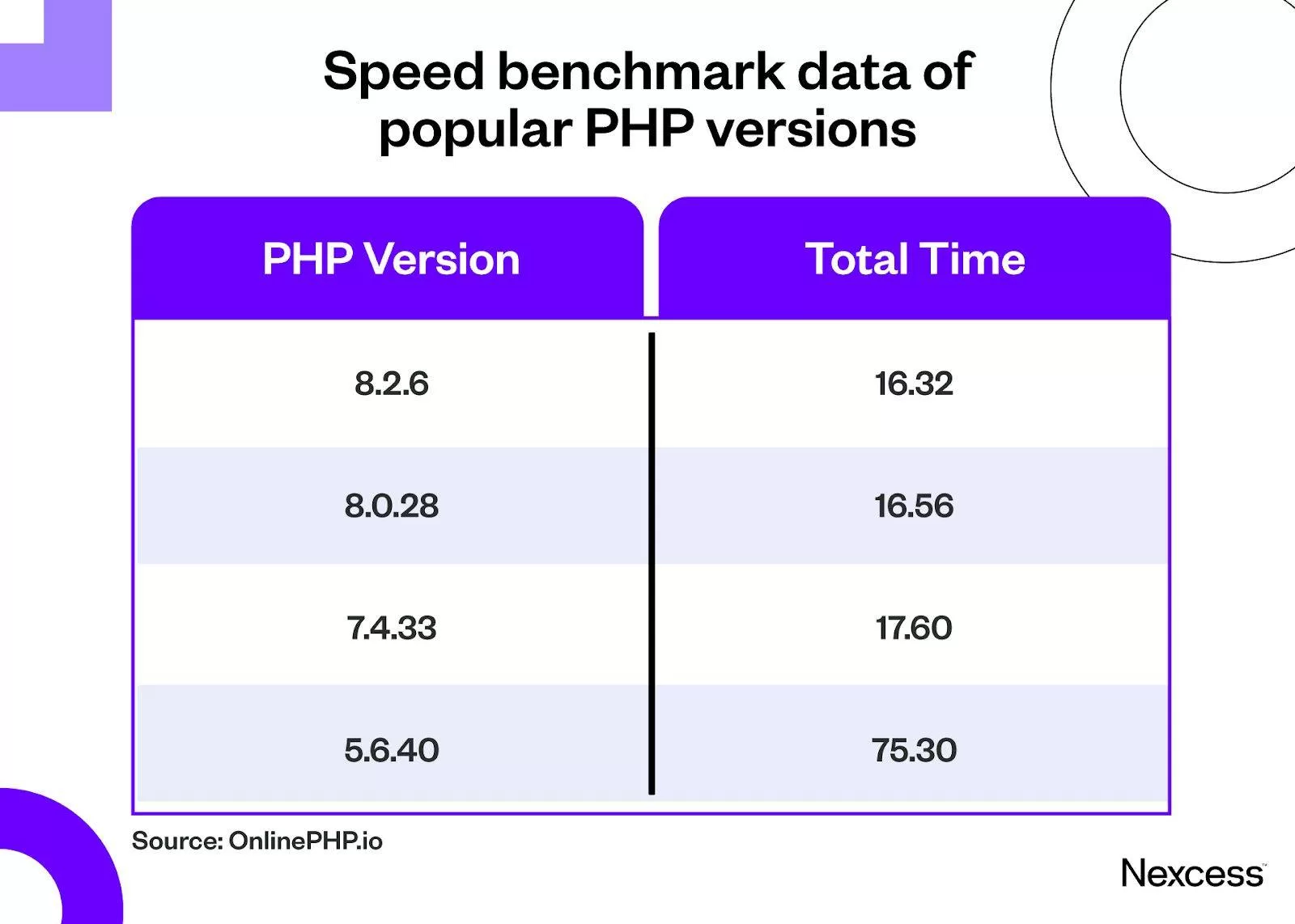
use the old version of PHP to slow down WordPress management? I will. In fact, PHP version 5.6 (the last version of PHP 5) runs almost five times slower than PHP version 7.4 or 8.0. Not to mention
, starting with WordPress 6.3, WordPress itself will give up support for PHP 5. So, if you’re still using PHP 5, it’s time to upgrade.
the following is a way to update the PHP version to speed up the WordPress management panel.
Through cPanel
if your host provides cPanel, you can use MultiPHP Manager to update PHP.
1. Navigate to the software section and open the MultiPHP Manager.
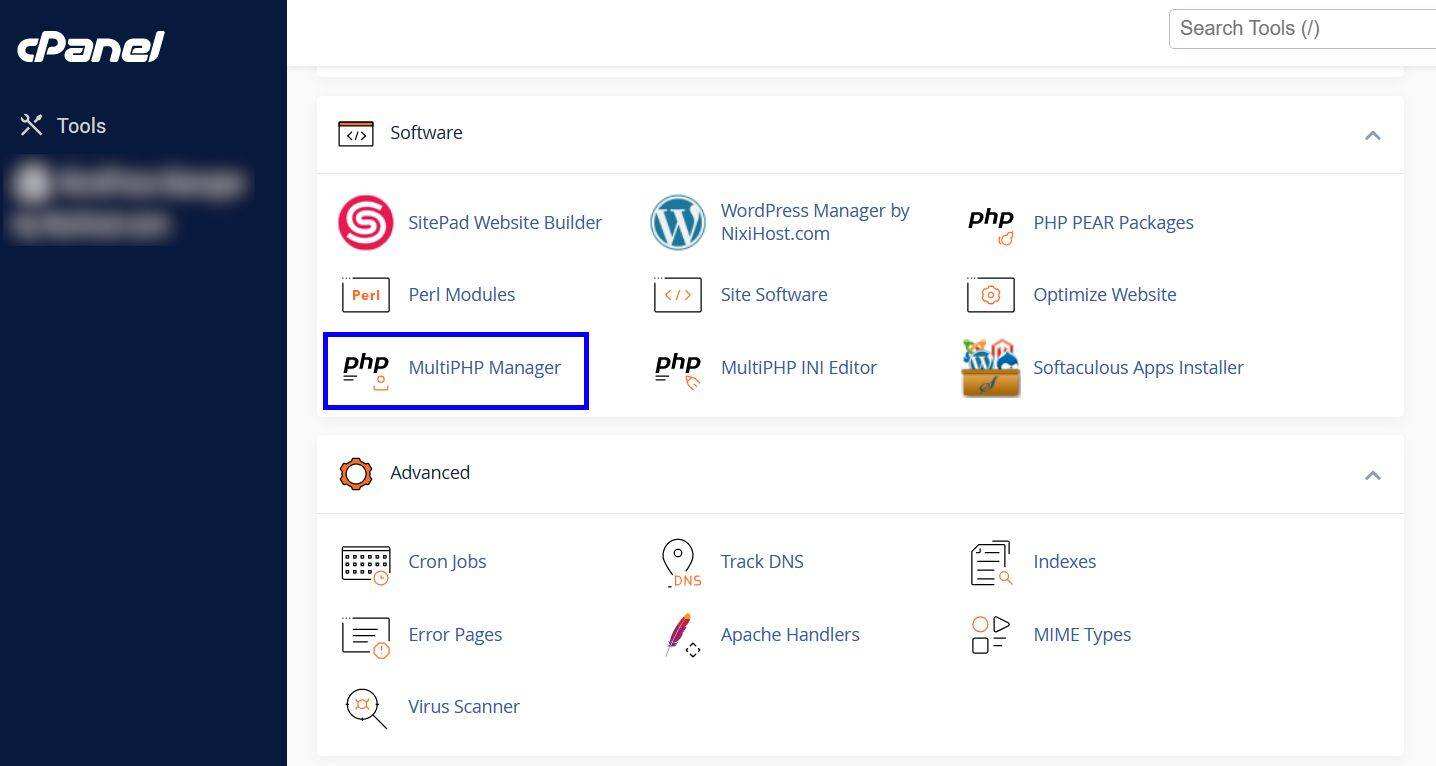
2. Check the check box for the domain name or website for which you want to upgrade PHP.
3. Open the PHP version list and apply the required PHP.

your host will update the PHP version in a few seconds.
Through the pagoda panel
Many
webmasters have installed pagoda panels on the server, and the pagoda also allows you to update the PHP version directly from the intuitive dashboard.
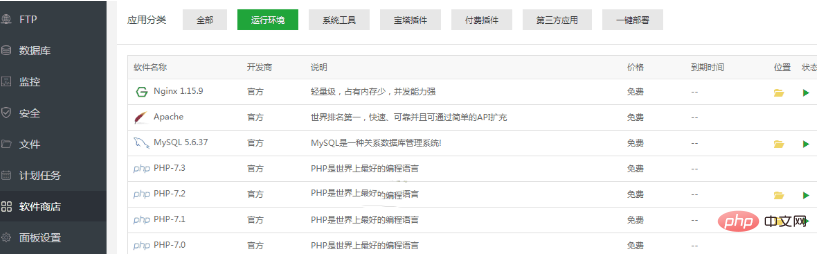
for example, the following is how to update the PHP version from the pagoda panel:
first, log in to the pagoda Web panel & gt;> Software Store & gt;> operating environment & gt;> installs the PHP version you want to switch. If you originally installed PHP7.1 and want to switch to PHP7.2, then directly click the corresponding “install” button on the right side of PHP7.2 and wait a moment to install successfully. The details are as follows:
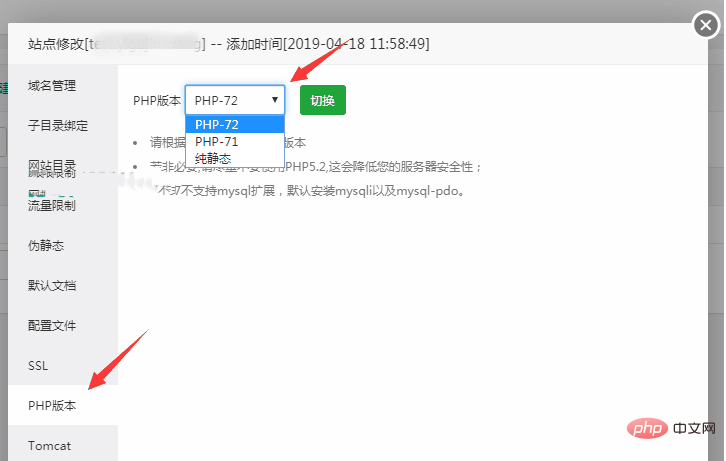
then click the left menu “website” & gt;> click the “Settings” button on the right side of the corresponding website & gt;> click the “PHP version” on the left & gt;> select PHP-72 & gt;> in the PHP version drop-down options and click the [switch] button, wait a moment to successfully switch the PHP version. As shown in the following figure: the
Pagoda Linux panel allows multiple PHP versions to be installed and run at the same time, allowing different websites to use different PHP versions. However, it is recommended that you try to run only one version of PHP, after all, running multiple PHP versions at the same time will take up resources.
It is recommended that after switching to the latest version, the unused PHP version can click “Settings” & gt;> click the “stop” button to stop it, or simply click the “uninstall” button to uninstall it, or install it if necessary.
By contacting technical support
if your web hosting provider does not provide the above options, please contact technical support. However, if the support team does not answer your question, or if the virtual host does not support the latest version of PHP, it is always a good idea to change to a better virtual host.
recommended reading: how to upgrade WordPress server PHP version
2. 0. Updating the WordPress kernel
almost every WordPress core update brings performance improvements and bug fixes, some of which are more recent than others.
for example, version 6.1 of WordPress, released on November 1, 2022, addresses more than 25 performance-related issues in WordPress. It improves WP_Query and changes the way PHP handles core block registration. Prior to
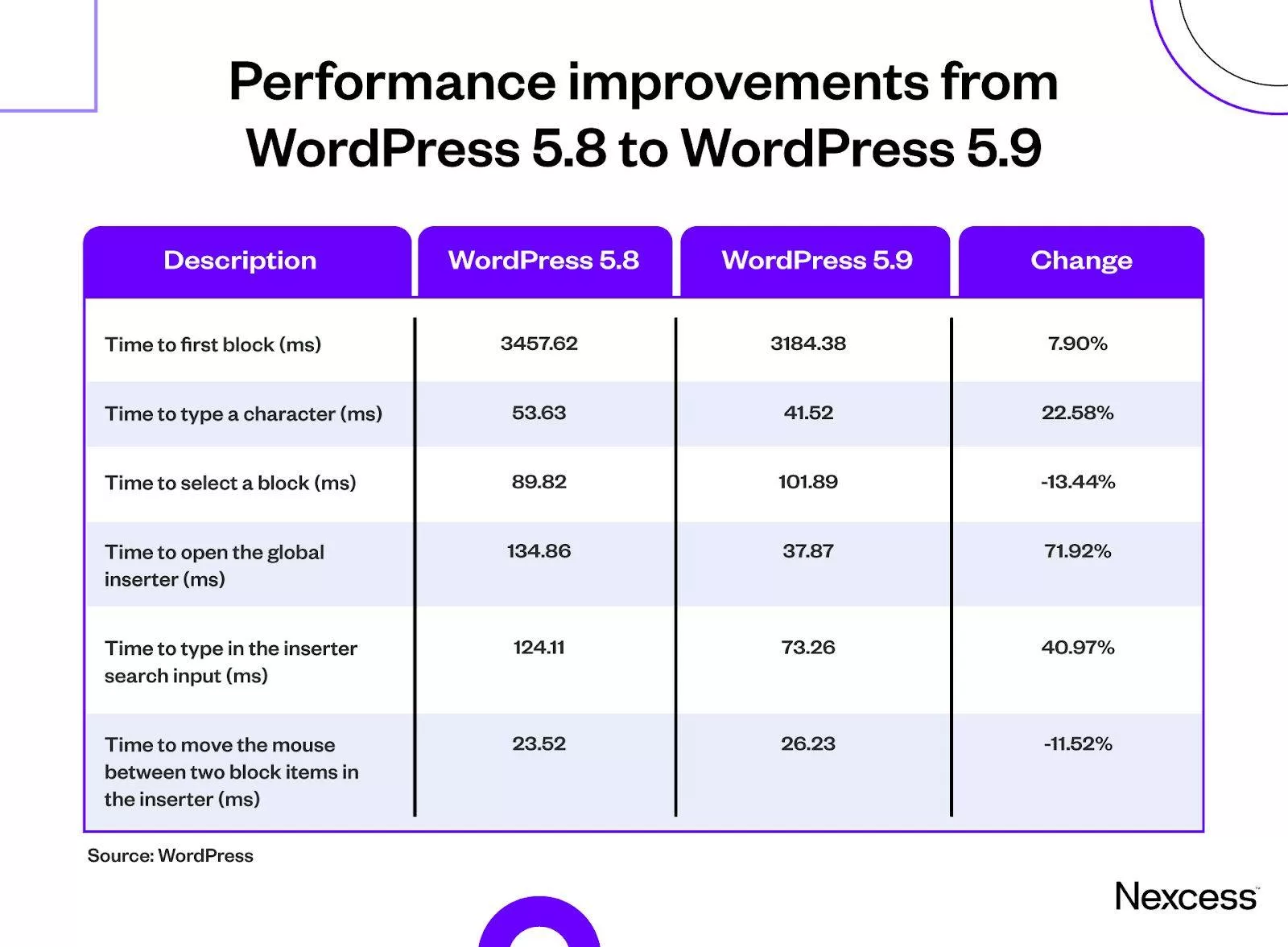
, WordPress 5.9 brought huge performance changes to management dashboards and WordPress editors. You can see the changes in the processing time of multiple editor-related tasks in the following table.
you can check your WordPress version by navigating to the tool & gt; site Health & gt; Information & gt; WordPress.
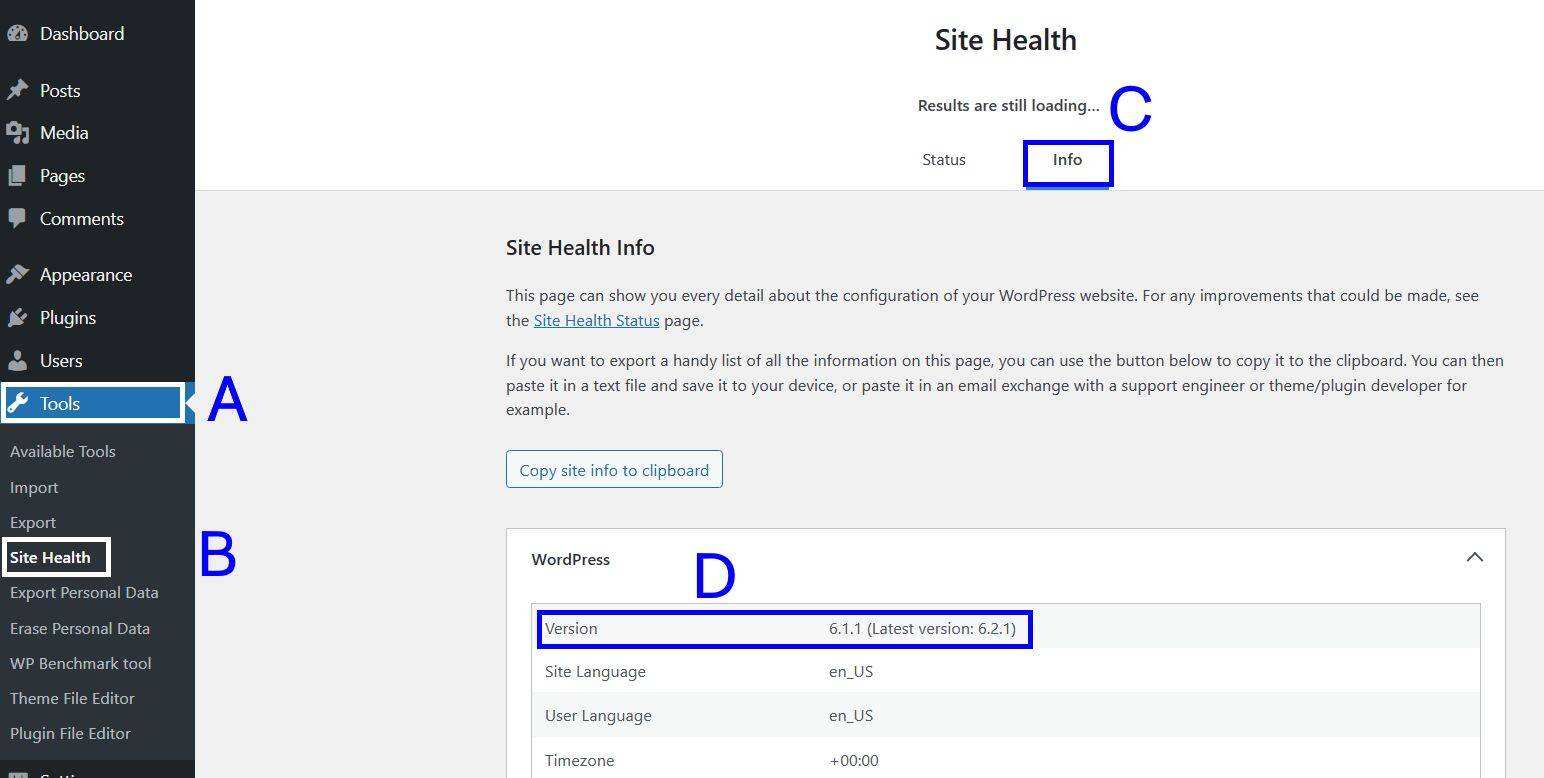
if your WordPress is out of date, you can navigate to the dashboard & gt; update via the WordPress dashboard.
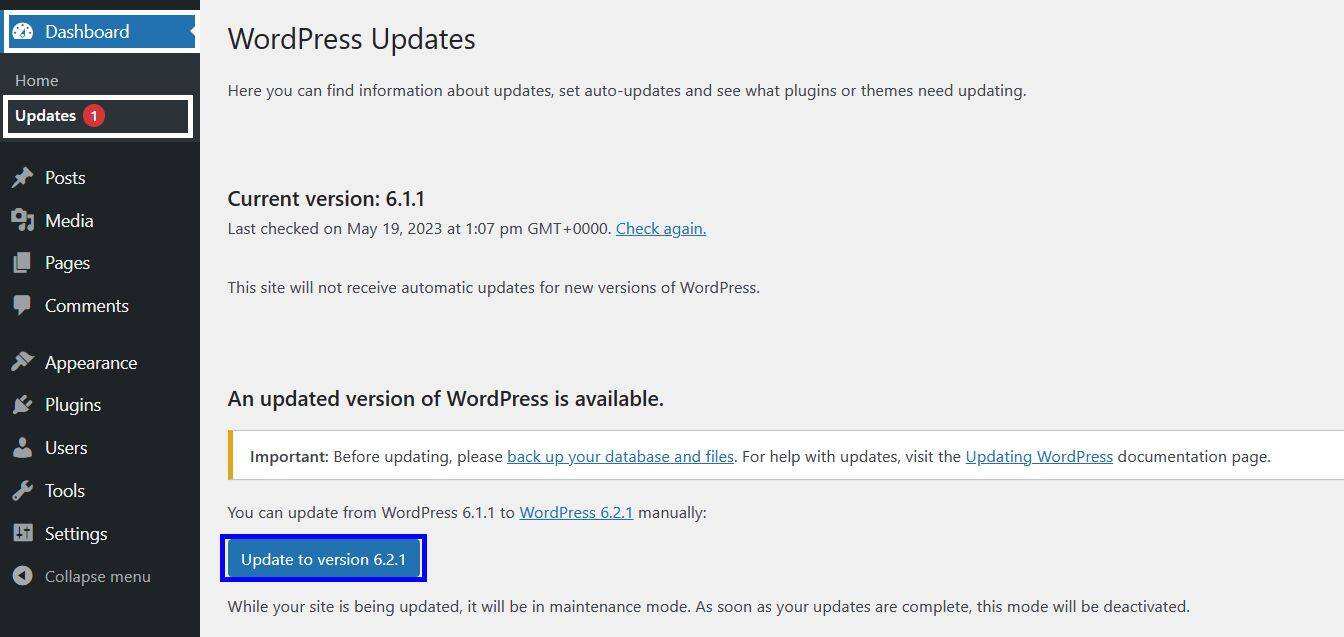
if you enable automatic update of the WordPress core, the system will do this automatically. You no longer have to worry about the WordPress kernel becoming obsolete.
3. Check your theme
WordPress theme to help you improve the visual effect of your site by adding custom layouts, unique typesetting, and feature-rich pages.
however, themes typically rely on functions.php files and integration plug-ins to provide these capabilities. Depending on how the features are configured and the plug-ins added by the theme, the management speed of WordPress may slow down.
you can switch to the default WordPress theme to see the impact of the theme on WordPress management. If it is a company or blog site, you can choose Twenty Twenty-Four. If you are managing a WooCommerce store, WooCommerce’s Storefront will be perfect for you.
, however, do not switch themes on the production site (that is, the version of the site that customers can see), as this will interfere with users who interact with the site. Instead, set up a WordPress staging site to troubleshoot themes without affecting the end user.
recommends reading: the fastest WordPress topic (based on comprehensive testing)
4. Remove bloated management functions the
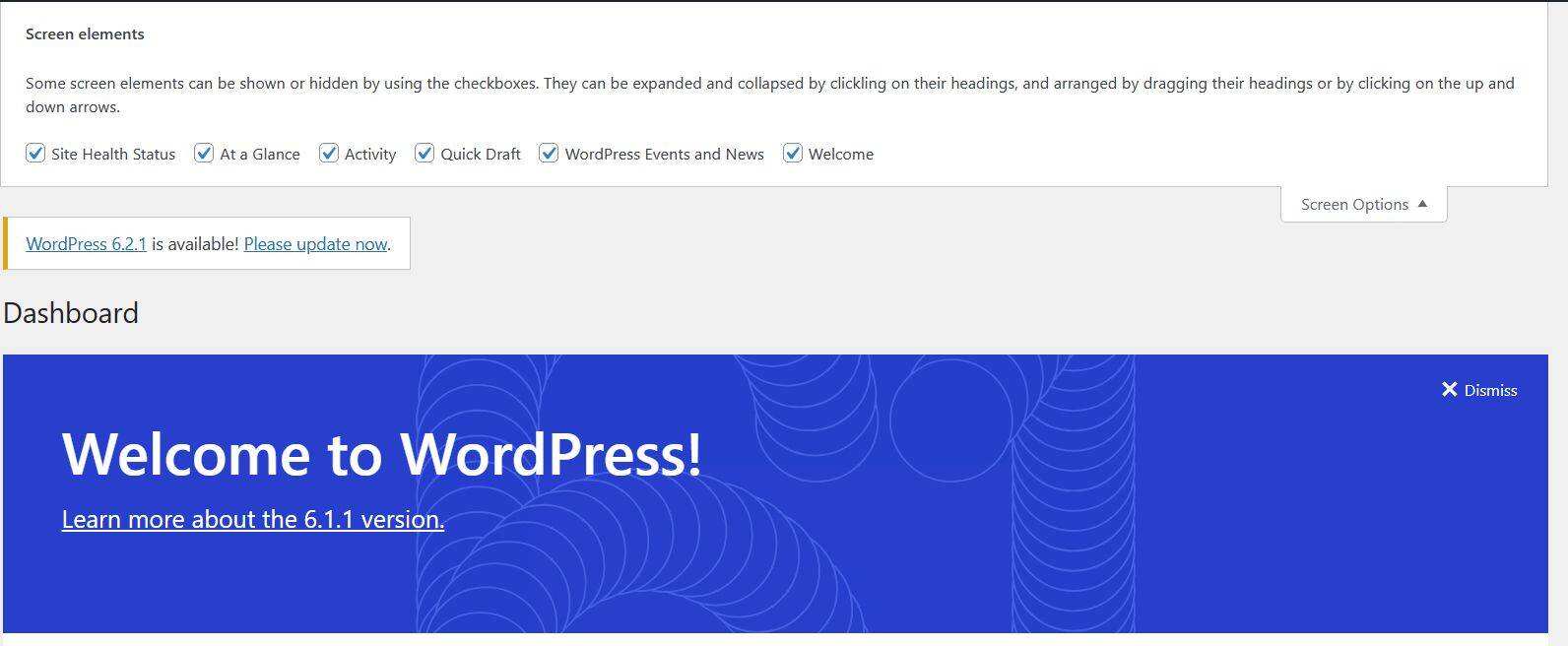
WordPress administrative panel has several bloated functions that you usually don’t need. For example, when was the last time you tried a quick draft or check WordPress events and news?
you can expand the “screen options” in the upper right corner to disable unnecessary dashboard widgets.
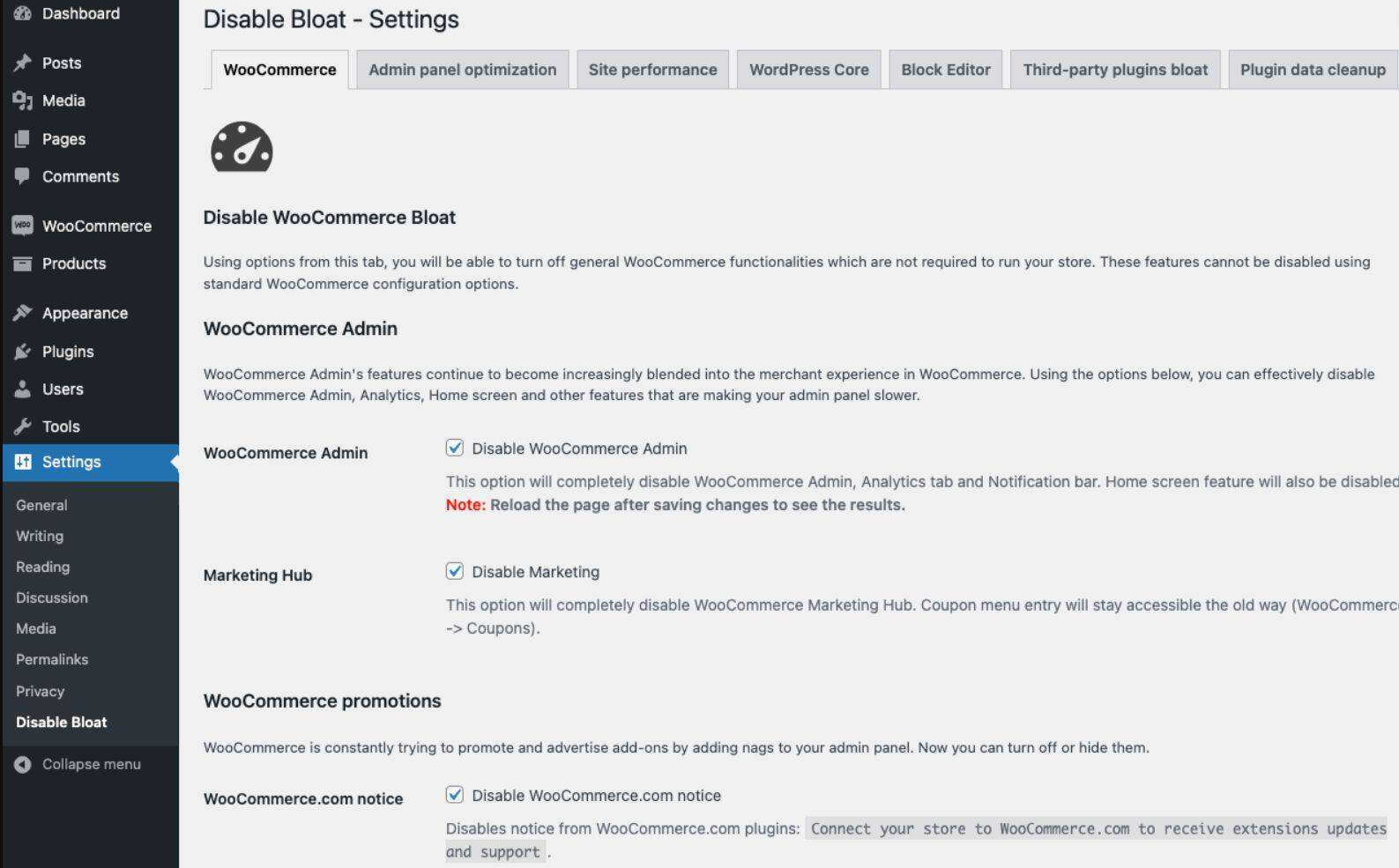
if you want more control over WordPress management, you can try plug-ins like Disable Bloat. With Disable Bloat, you can disable unnecessary features of both WordPress and WooCommerce.
5. Replacing plug-ins with excessive memory consumption
is notoriously skewed on the demand side in the supply-demand equation. Not only uncommon plug-ins, but even well-known plug-ins can slow down WordPress management.
you can use monitoring tools such as Query Monitor to find a large number of plug-ins used by WordPress websites.
for example, you can use Query Monitor to see the impact of each plug-in on load time:
- Click the Query Monitor menu on the management toolbar.
- goes to “Queries by Component”.
- sorts by time to see the plug-ins that consume the most resources.
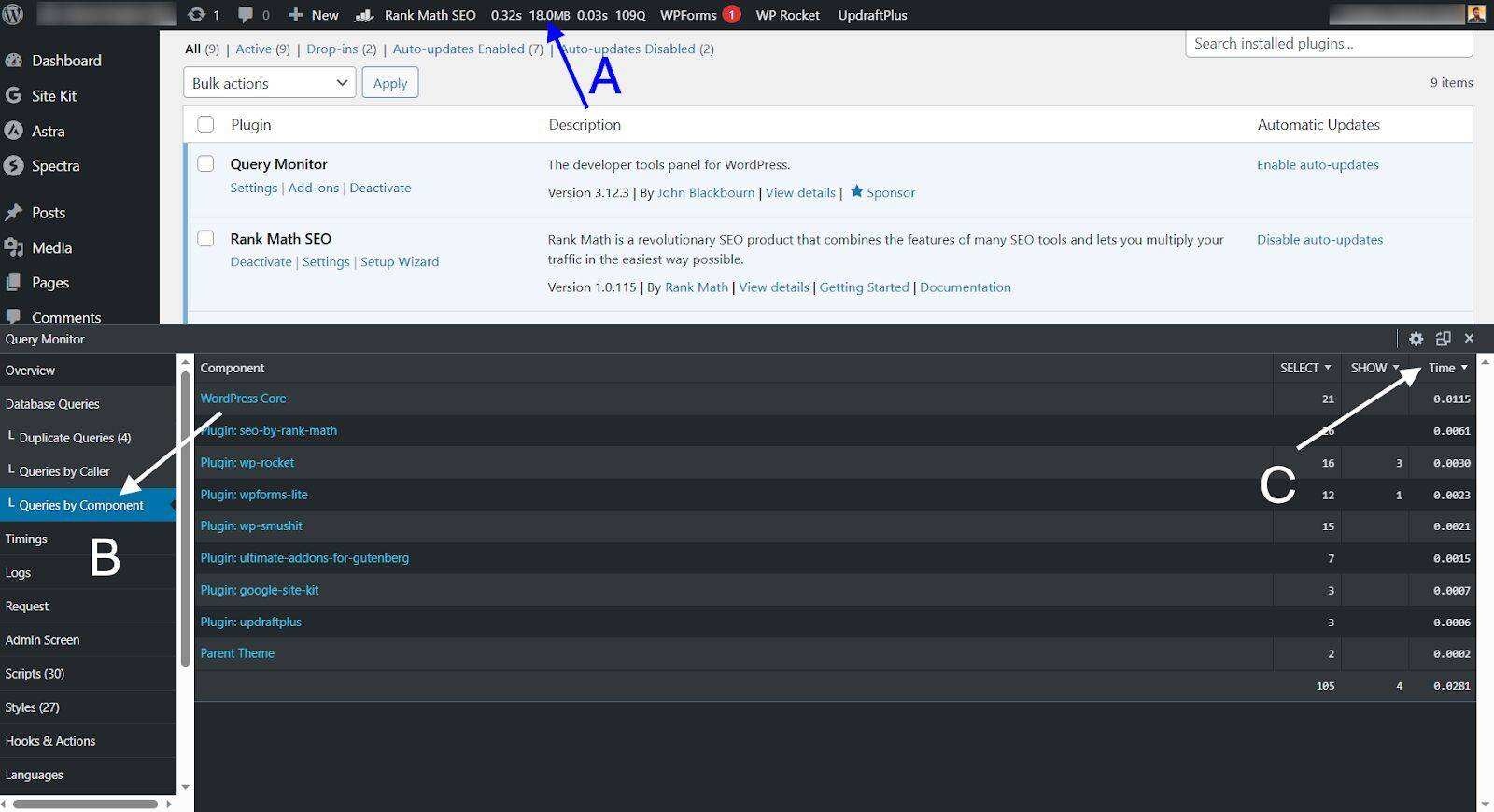
if demanding plug-ins are not required, uninstall them immediately. If they add the necessary functionality, use WP Hive’s Chrome extension to find alternatives in the WordPress plug-in library.

6. Increase PHP memory limit
even if you buy the latest truck, you can’t use it if the street is too narrow. Similarly, the latest version of PHP may not help if the memory limit of PHP is too low. The PHP memory limit is the amount of memory that can be used by PHP scripts on the WordPress website.
is in Nexcess, and we recommend that you run WordPress with at least 256MB memory installed on PHP. If your WordPress configuration value is low, you should increase the PHP memory limit to allow breathing space for the WordPress core and installed plug-ins.
is the same as the PHP version, you can also check the PHP memory limit of the WordPress site by navigating to the tool & gt; site Health & gt; information and expanding the server.
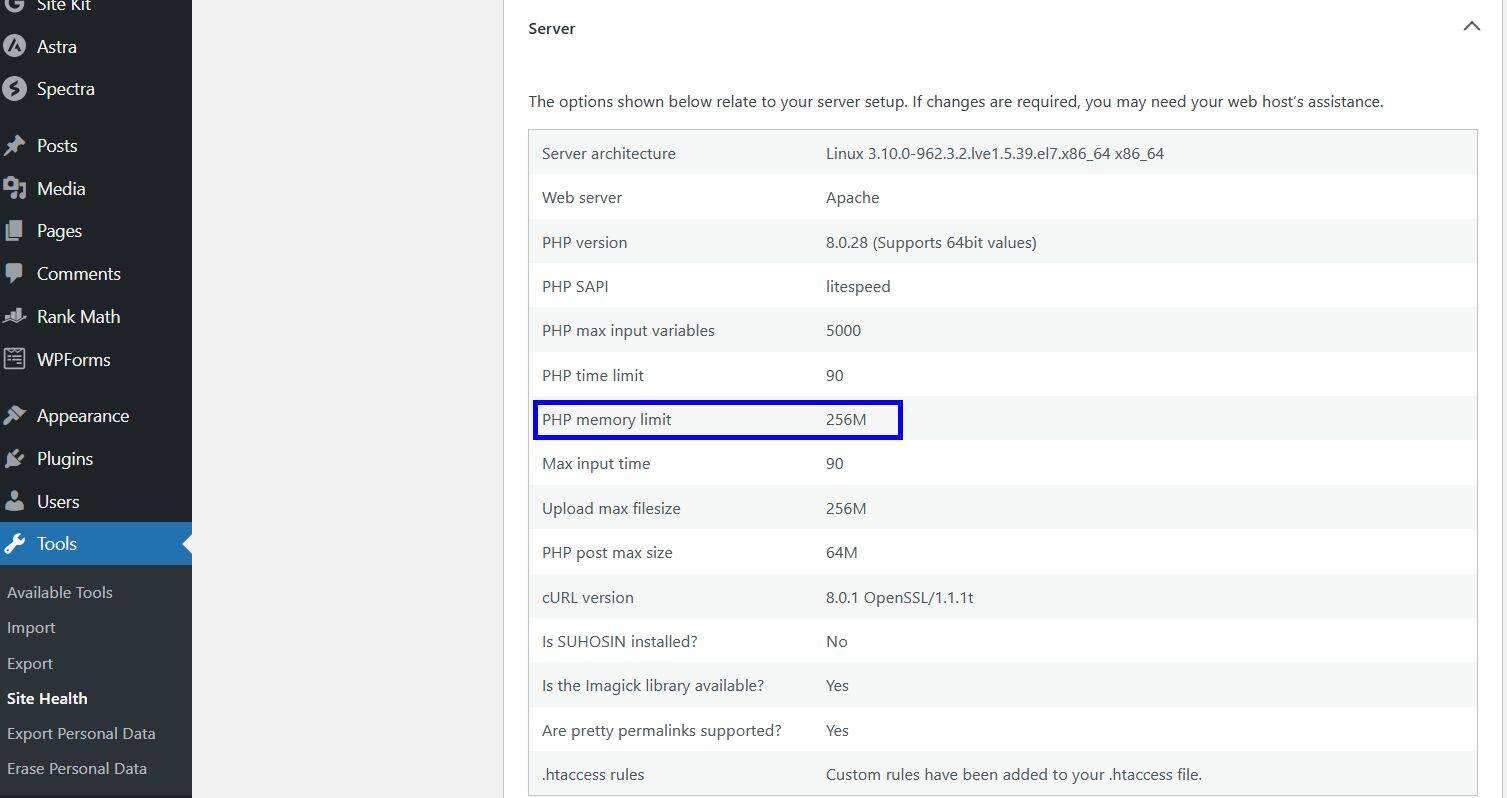
in this example, the memory has been set to 256MB. If your settings are low, you can use cPanel’s MultiPHP INI editor to increase the PHP memory limit. After

enters the MultiPHP INI editor, use the drop-down menu to select the WordPress site, write 256m in the memory_limit field, and then apply the changes.

if your host does not provide cPanel, you may need to edit the wp-config.php file or contact customer support for help.
recommended reading: how to increase PHP memory limit
7. Enable persistent object caching
due to the ever-changing WordPress hypervisor, the typical caching mechanism does not apply to WordPress dashboards. In other words, page caching and browser caching don’t help.
however, an object cache that caches frequently accessed information can cache frequently accessed data objects. In particular, it can provide the required data objects for the WordPress management background to load quickly.
You need a persistent object cache to benefit from it. If your virtual host supports Redis or Memcached, you can enable them to add persistent object caches. Alternatively, you can install Docker Cache.
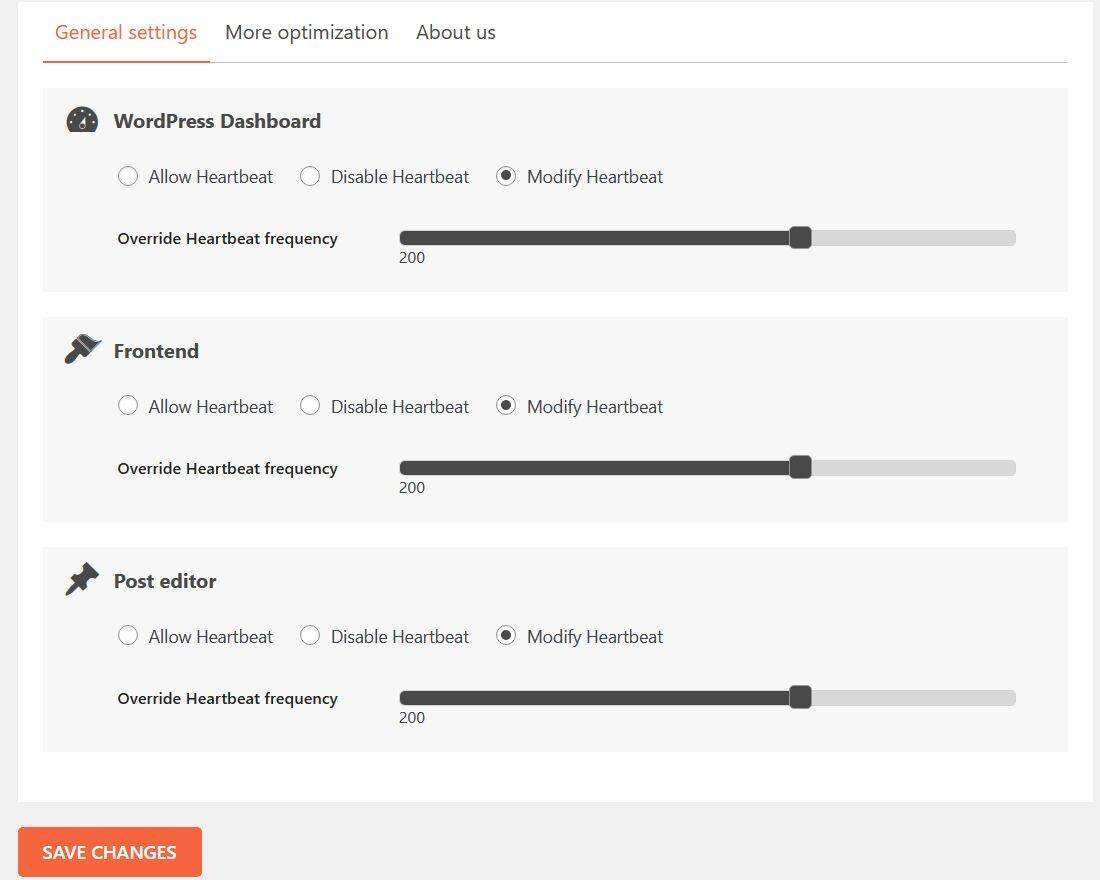
8. Increase the interval between Heartbeat API calls
WordPress relies on the heartbeat application programming interface (Heartbeat API) to facilitate real-time communication between web browsers and servers. In other words, the changes you make on the backend will be registered with the server through Heartbeat API.
in particular, Heartbeat API can help WordPress exchange the following information:
- the changes you made on the content editor.
- notifications about e-commerce orders, comment submissions, and plug-in updates.
- updates on article activity-whether someone is editing an article.
although you don’t want to delete the entire draft because your computer crashes, so you want to get all of this information, sending regular AJAX requests can put pressure on the WordPress management background.
for example, if the user is working in the editor, the WordPress management background sends an AJAX request every 60 seconds to automatically save the draft. On the other hand, the articles page is usually synchronized every 15 seconds to prevent two users from editing the same article. If
has multiple users working on your WordPress site, all of these requests will almost paralyze your WordPress management.
if you are using shared WordPress hosting, your hosting service provider may even suspend your hosting service because of high CPU utilization. So, what’s the solution? Increase the interval between calls to Heartbeat API.
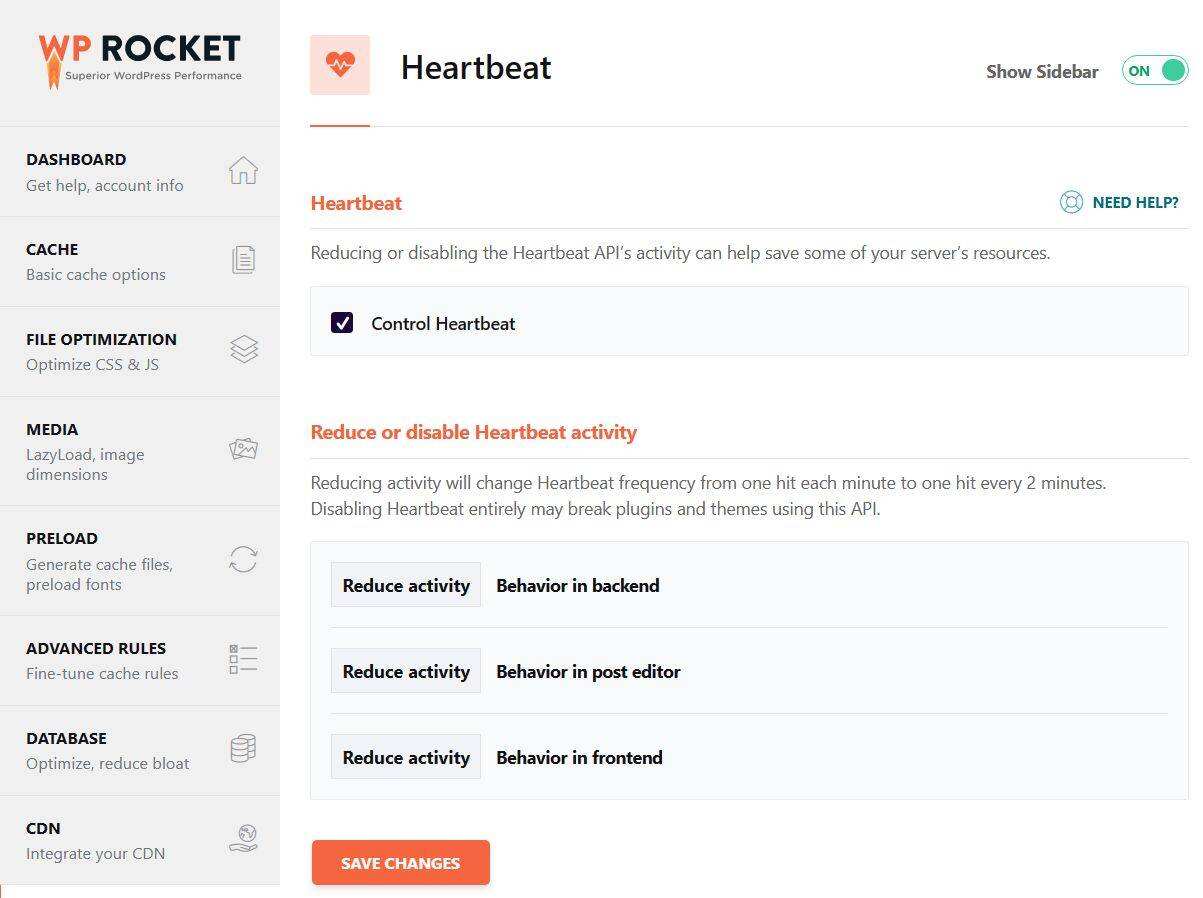
you can use WP Rocket’s Heartbeat control plug-in to adjust Heartbeat API settings. After installation, increase the Heartbeat frequency as needed. In general, it works well in the range of 100-200 seconds.
9. Deleting a bloated database
is like a temporary folder for Windows that fills up every few months, so WordPress and its plug-ins generate a certain share of bloat.
in particular, different plug-ins use registers to cache and store temporary data in WordPress databases. Because the plug-in does not need to regenerate the required data, these staging data can help improve the performance of WordPress.
registers usually expire after a certain time and become expired registers. They remain in the database until they are requested again. However, “until” may mean an hour, a day, or a year, depending on the plug-in.
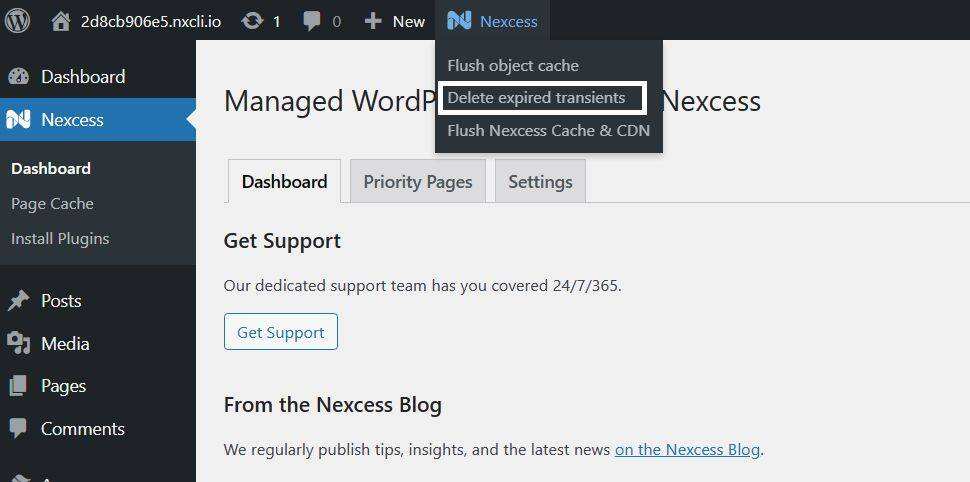
, for example, WooCommerce has filled WordPress databases with expired staging information. To delete these expired temporary files manually, you can use the Delete Expired Transients plug-in.
in addition to out-of-date temporary files, you may also need to deal with revised versions of articles. Each time
saves a post or page, WordPress creates a revision of the post that you can use to restore as needed. Although they may be helpful in making articles, they will be of little value when you finally finish the article.
you can use plug-ins such as WP-Optimize to remove these additional article revision history.
10. Install the WordPress caching plug-in
although caching plug-ins usually deal with the front end of a Web site, they also mean good news for the WordPress management background.
in particular, the WordPress caching plug-in caches dynamic web pages in the form of static HTML, reducing the need for repetitive and resource-intensive processes. As a result, your WordPress site can provide more CPU available to the WordPress management background.
WP Rocket may be a good choice for caching plug-ins because it is an all-in-one solution that can also help configure Heartbeat API and remove database bloated.
11. Limit the number of articles or comments per page
by default, WordPress displays a maximum of 20 articles, comments, or custom article types (such as WooCommerce orders) per page. However, if you have increased the number of projects in the past to avoid paging, this number may be even higher.
projects that load less always take less time than projects that load more. Therefore, if you encounter the problem of slow WordPress management, try reducing the number of items per page from “Screen Options”.
12. Time to monitor the first byte time
first byte time (TTFB) is the time it takes for the web browser to receive the first byte from the server after sending the request. Although it is usually a network metric for testing the front end of a WordPress site, you can also use it to test the back end.
in particular, if the TTFB is too high, it means that the administrative area can even take a long time to send the first byte. In addition, if your TTFB is high, it means you are using resource-intensive plug-ins, or your hosting infrastructure is not suitable for your site.
13. Change to a better managed service provider
in the previous 12 tips, we have explored a variety of ways to reduce the demand side. However, there is a limit. You can’t expect to run a growing e-commerce store on a shared WordPress hosting plan without problems.
, in other words, if none of these techniques can help you speed up WordPress management, then you should look for a better hosting infrastructure with competitive technical specifications, advanced performance add-ons, and content delivery networks (CDN) in the industry to uninstall intensive processes.
in addition, look for hosts that can provide the following functions:
- PHP 8 compatibility: given the improved performance of each new PHP version, you should not choose a virtual host that does not support the latest PHP version.
- Performance monitoring tools: if you rely on external performance monitoring tools, you often don’t know how much burden each add-on brings until your WordPress management is slow enough to crawl.
- Staging site: you should not do all the testing on a real-time website. Make sure that the web hosting company provides a free staging site.
summary
website management task is numerous, already difficult enough. You don’t want to make it harder to manage the background with a slow WordPress. The above 13 methods of
are probably the most direct and common, and you can certainly take more feasible measures to improve the speed of WordPress background. For example, if you install the WordPress performance optimization plug-in-WPTurbo, you can also refer to the following article:
- WordPress website page speed optimization beginner’s guide
- WordPress website speed optimization ultimate guide
- how to achieve the full score of Google PageSpeed Insights test