
As a marketer, you may spend hours or even days making the perfect email. However, if your mail ends up in a spam folder, your latest activity is almost certainly dead in the water.
Fortunately, there is a way to avoid the terrible black hole in spam folders. By implementing email authentication, you can prove to your Internet service provider (ISP) that your marketing email is legitimate and should have a place in the recipient’s inbox.
This article will discuss what email authentication is, why it is so important, and how it works. Then we’ll show you how to implement it in the three most popular e-mail marketing tools.
- What is email authentication (and how it works)
- Five main email authentication methods
- How to set up email authentication
- Monitor your email authentication health
What is email authentication?
Nobody likes spam. ISP has been trying to reduce the amount of spam we receive in our inboxes. They do this by checking the source of the e-mail and verifying whether it comes from a legitimate sender or a potential spammer.

This is the opportunity to use your talents for e-mail authentication. It is a set of methods that the receiving server can use to verify that the message is not bogus.
As part of this check, the server verifies that the message is from the person listed in the from field. In this way, e-mail authentication prevents spoofing and phishing fraud, where e-mail appears to be from a legitimate domain but is sent by a malicious third party.
The recipient server will also determine whether the e-mail has changed during transmission. This protects your contacts from middleman attacks.
There are several ways to implement e-mail authentication. Each method has its own setup process and makes unique adjustments to authentication. However, you usually establish rules to validate e-mail messages sent from your domain. You will then configure your server and email infrastructure to implement these rules, and then publish them to the Domain name system (DNS) record for each shipping domain.
The receiving email server can refer to these rules when validating incoming e-mail. If your message looks legitimate, the server sends it to the recipient’s inbox. However, if your message fails this check, it may be rejected, quarantined, or sent directly to spam.
Why email authentication is important
For the recipient, email authentication has a clear purpose. It helps protect users from spam, phishing scams, and other malicious emails.
Without authentication, third parties can easily change the e-mail source to bypass the spam filter. They may even copy your unique brand to induce your customers to believe that this is a legitimate communication.
Any attack that impersonates your business is a huge threat to customer trust. As a result, email authentication is a key tool to protect your reputation and retain your audience.
Authentication increases the chances that the receiving server will trust your e-mail. By contrast, if your messages seem to come from an unknown or unexpected domain, they are likely to enter the spam folder.
Poor email delivery rates almost inevitably translate into low return on investment (ROI) in content marketing. By implementing email authentication, you should be aware of the positive impact on email conversion rates.
Today, many enterprises use third-party platforms to send email, such as Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or other alternative tools. You can use these platforms to create automated activities and perform subdivisions.

Mailchimp
By verifying your domain and email, these platforms can send messages from your site’s domain on your behalf. For example, Mailchimp removes the default authentication information that appears next to the from field of your activity (through mcsv.net or on behalf of mcsv.net). This can increase your brand awareness and may encourage your contacts to open your email.
You may be worried about adding a lot of complex content to your e-mail. However, most authentication information is transmitted in the header and is therefore not visible. This means that authentication should not affect the quality of your email content.
Five main email authentication methods
E-mail authentication requires coordination between the sending and receiving servers. Fortunately, the email authentication standard ensures that all e-mail clients and providers use the same language. Before we show you how to implement authentication, let’s take a look at these underlying standards.
1. DKIM/ domain name key
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) provides a unique public key paired with the private key. This DKIM signature is a header added to the message and protected by encryption.
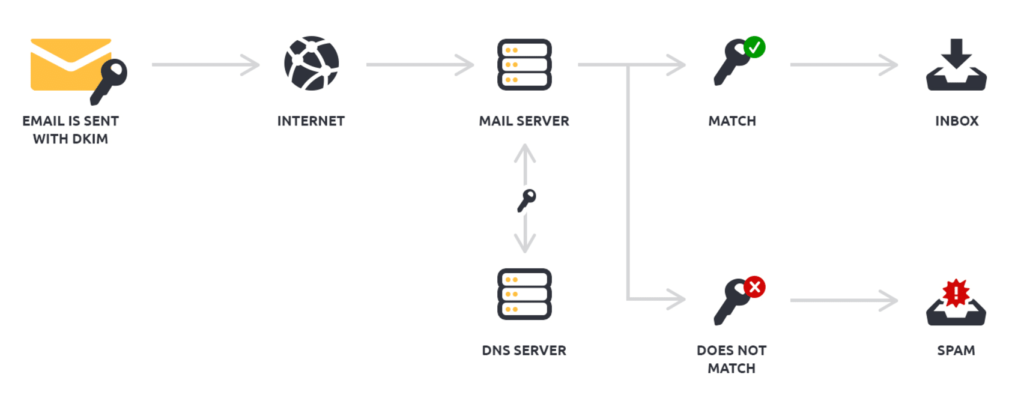
How DKIM authentication works (image source: Mailjet)
In this way, DKIM can verify that the e-mail came from a legitimate sender. As part of an intermediate attack, DKIM signatures can also prevent hackers from tampering with e-mail during transmission.
This is an example of the DKIM record that Mailchimp uses for authentication:
CNAME record: k1._domainkey.yourdomain.com
Value (parsed to): dkim.mcsv.net
At the same time, this is an example of a DKIM record with MailerLite, using TXT records:
TXT Name: ml._domainkey.yourdomain.com TXT Value: k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDdgIGns7EFVltvAkNNdbXD9KYSzAUNQky8POXwH6
Typically, DKIM signatures are not visible to recipients because verification is performed at the server level. This means that adding DKIM records can improve your delivery rate without affecting the quality of your email.
2.SPF
The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an authentication standard that verifies your identity as the sender of an e-mail message. This policy compares the IP address of the outgoing mail server with the list of IP addresses that are authorized to send mail from that domain. The SPF record is added to the sender’s DNS.
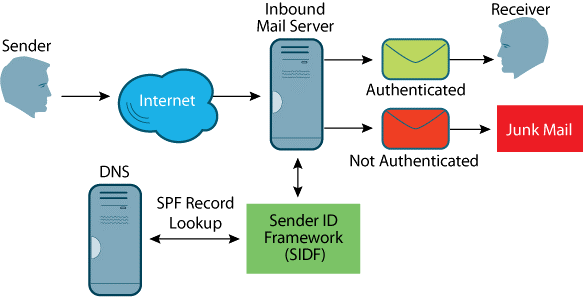
How SPF authentication works (Img src: Inside-Out)
Whenever the server receives an email, your ISP uses the SPF record to check the sender’s IP address. Assuming that this value matches the SPF record, the email will be sent successfully.
If you do not provide SPF authentication, the recipient server may reject your messages because they are from an unverified sender address. The following is an example of the SPF TXT record that Mailchimp uses to perform email authentication:
v=spf1 include:servers.mcsv.net ?all
Some of the largest companies in the world use SFP, including Google, Comcast, Verizon, Live.com and Cox.net.
3. Sender ID
Sender ID, developed by Microsoft, is often confused with SPF. Both sender ID and SPF check the sender’s IP address against the registered owner of the domain. However, their methods are slightly different.
The sender ID uses the claimed responsible address (PRA) algorithm to check the sender address that is visible in the message. Let’s look at an example of a Sender ID record:
v=spf1 include:servers.mcsv.net ?all spf2.0/pra include:servers.mcsv.net ?all
Sender ID is mainly used by Hotmail and Windows Live Mail, both of which no longer exist. Because it is not widely adopted, Microsoft has deleted the official Sender ID website.
Although it is easy to think that the sender ID is obsolete, it is still used in some solutions, especially the internally deployed Microsoft Exchange server. Some ISP, such as Comcast and AT&T, also use Sender ID.
4. DMARC
Domain message Authentication report and Conformance (DMARC) is a policy for handling e-mail messages that are not authenticated by SPF or DKIM. This gives you more control over your email authentication system and helps protect recipients from phishing and spoofing attacks.

DMARC (photo source: DMARC.org)
Using DMARC, you can tell the receiving e-mail server how to react when it receives a message that appears to be from your domain but does not pass the SPF or DKIM authentication requirements. The following is an example of a DMARC record using TXT records:
v=DMARC1;p=reject;pct=100;rua=mailto:yourdomain.com
You can also use DMARC to request reports of failed messages and potential spoofing of domains from your e-mail server. These reports can help you identify any authentication problems and malicious activities related to messages sent from your domain.
5. Brand indicators for message recognition (BIMI)
The Brand Metrics for message recognition (BIMI) standard appends your brand logo to an authenticated email. Behind the scenes, a BIMI is a text record stored in your DNS record, containing the location of your company logo.
The e-mail provider will use DNS lookup to retrieve your BMI text record when it receives the message. Once the provider finds your logo, it will attach the graphic to the email in the recipient’s inbox.
This simple visual verification helps the recipient discover your message and verify its authenticity. If they receive a message that does not contain your logo, your contact will immediately know that this is a suspicious message.
Unlike other verification methods we have explored, BMI is the only way to provide visual clues to the recipient. This should also cause fewer people to mistakenly mark your mail as spam, thus improving your delivery rate.
The typical Internet user receives dozens or even hundreds of emails every day. By displaying your logo in the recipient’s inbox, BIMI can help you attract the recipient’s attention and encourage them to interact with your email.
Whether an individual chooses to interact with your information or not, BIMI can also be a way to market your brand. Even if this person never opens your email, they will still see your subject line, sender’s address, and logo. This is a good way to build brand awareness.
How to set up email authentication
Email authentication may sound complex, but it is relatively simple to set up. Even if you have previously implemented authentication and have been using the same email marketing tool for some time, it is still wise to ensure that the correct records are in place and verified.
If you recently changed your DNS provider, you need to check your records, as this can easily affect your e-mail authentication. One of our customers recently relocated the DNS provider and their newsletter was sent directly to the spam folder for nearly a month until someone realized it. This is due to the lack of authentication records.
As a result of this mistake, their opening rate is 4.79% lower than last month, and the click-through rate is down 1.56. This perfectly explains why you can’t risk sending mail to spam.
Let’s make sure this doesn’t happen to your email. Here is how to set up authentication for the three most popular e-mail platforms.
1. Mailchimp
Today we’ll show you how to set up email authentication in MailChimp, one of the most famous and widely used email marketing tools on the Internet. No matter which email marketing solution you currently use, the following process will be very similar.
Step 1
Log in to MailChimp and hover over the avatar in the upper right corner. Click “Account”.

MailChimp account
Step 2
Click Settings, and then click Verified domains. If you have never set it, you will need to click Verify a domain. Otherwise, you will see a list of currently verified domains and green / red indicators to show whether they are currently validated.
Domain validated by MailChimp
Step 3
Enter the email that resides on the domain you are trying to validate. Then click “Send Verification Email”. If you do not have an e-mail address in your domain, we recommend that you use Google Workspace (only suitable for foreign trade websites or websites for foreign users, the server is located abroad).

Send a verification email
Step 4
Click the validation link you received in the email or enter the CAPTCHA manually.

Verification domain
Step 5
MailChimp will then provide you with DKIM and SPF DNS records that you need to add to successfully complete domain authentication. You can add these through your DNS provider or domain registrar.

MailChimp domain authentication record
In our example, we will show you how to use DNSpod to do this. Whether you are using another third-party DNS provider or your domain registrar, this will be very similar. In DNSpod, just click “DNS Resolution-my Domain name” on the left. Then click the domain name you want to manage.

Manage DNS in DNSPOD
Step 6
Click add record at the top.
Add DNS record
Step 7
We first need to add the CNAME record using the values in MailChimp. This is used for the DKIM authentication method.
For the record type, select CNAME from the drop-down list. In the Host record field, we enter the following. Most DNS management tools automatically attach domains. Therefore, be careful not to enter the entire value provided to you by MailChimp.
k1._domainkey
In the record value field, we enter the following:
dkim.mcsv.net
Then click OK.
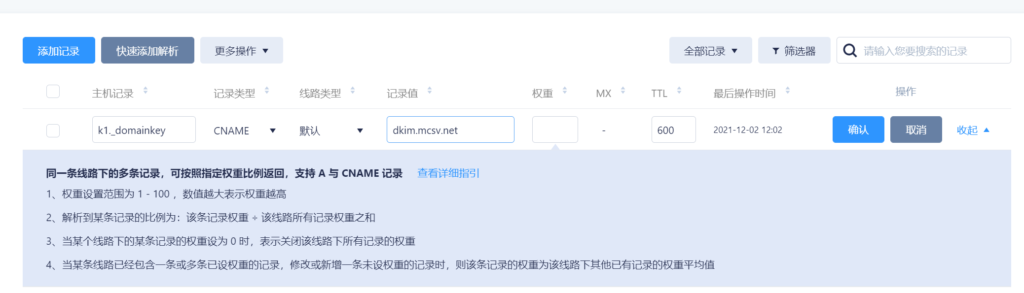
Add CNAME for DKIM
Step 8
We now need to add the TXT record using the values in MailChimp. Click add record again. This is used for the SPF authentication method.
For the record type, select TXT from the drop-down list. Leave the Host record field blank so that it will only use the root domain. Then enter the following in the record value field:
v=spf1 include:servers.mcsv.net ?all
Then click add record.

Add TXT records for SPF
Step 9
Return to MailChimp and click “Authenticate Domain”.

Domain authentication
It may take some time for DNS records to spread. If it doesn’t work immediately, you can go back later and try. Or you can use whatsmydns to verify the status of your records.
For example, you can enter your CNAME to check the current value worldwide.

Verify DKIM record
You can also view your TXT records.
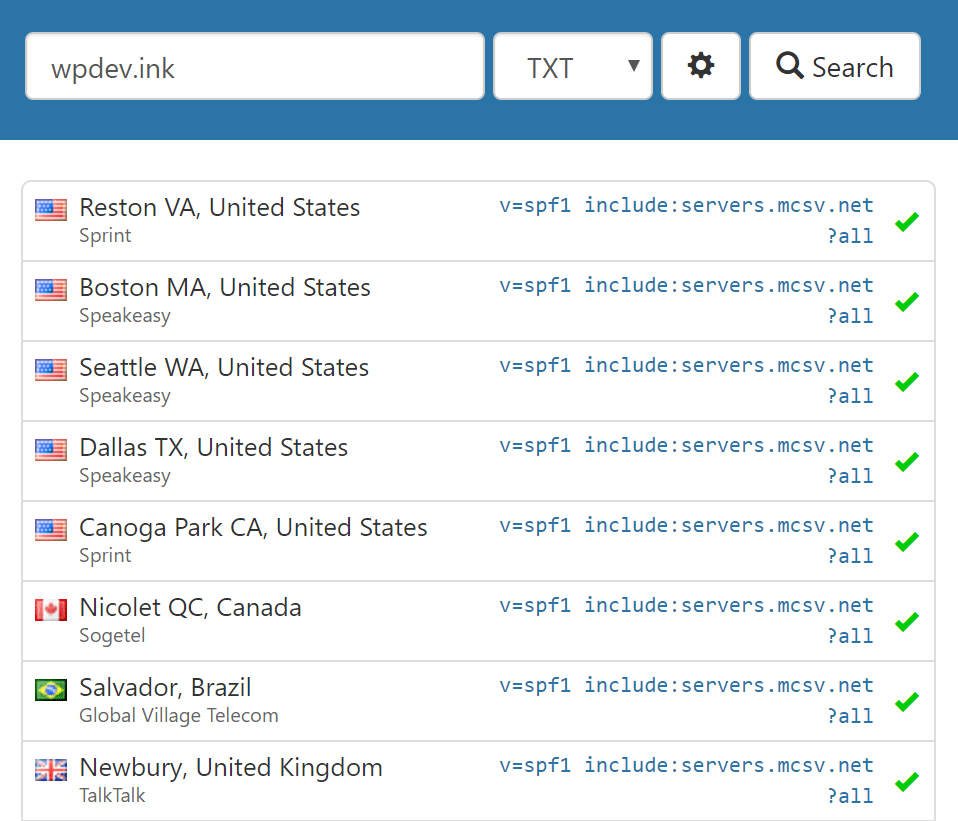
Verify SPF record
If all the records are entered correctly, you should see the whole line green.

Verification domain
okay! Your email and domain are now authenticated. It is also recommended that you change the sender address in the list to your domain name.

List name default
2. Constant Contact
Constant Contact is a popular email marketing application that provides an excellent alternative to Mailchimp. The tool has a wide range of mobile optimization templates and intuitive editing tools.
After you start your activity, you can track it in real time using Constant Contact’s built-in analysis and reporting tools.

Constant Contact
All messages from Constant Contact have been signed by DKIM and should be checked by SPF. However, the company recommends that you enable continuous contact authentication. This allows you to register as an authorized sender from the Constant Contact mail domain.
Continuous contact authentication can enhance your brand image and enable your message to be identified by the recipient. This minimizes the number of people who mark your message as spam.
Log in to the Constant Contact dashboard and select My Account to activate this feature. In the My Profile section, navigate to Campaign Email Authentication Settings & gt; Enable Authentication with Constant Contact.
You can now enter the e-mail address you want to verify, including free web mail addresses, such as those from Gmail and Outlook. After entering your address, click Save. Note that it may take up to 24 hours to configure an account using authentication, so you may need to wait.
Whenever you send an email, ISP will see your sender header address in the email. It will then check your published authentication record and confirm that you are a legitimate sender.
Note that the recipient can see the Sender Header Address, although its appearance may vary from email client to email client. However, your Reply-To-Address value remains the same, so any reply will be sent directly to your email address instead of contacting the server frequently.
3. HubSpot
HubSpot’s email marketing tool, powered by the popular customer relationship management (CRM), has everything you need to create a professional-looking marketing campaign. After you have designed your email, HubSpot will provide Amax B testing and analysis, which you can use to optimize your activities and provide the best results.
If you want to send mail from your domain using DKIM e-mail authentication, you can connect your e-mail sending domain to HubSpot. The first step is to verify your domain in your HubSpot account. In the HubSpot dashboard, click the Settings icon in the main navigation bar.

Click “Settings” in the HubSpot dashboard
Next, navigate to Website & gt; Domains & URLs & gt; Connect a domain. In the next dialog, select Email Sending, and then click Connect. You will now be directed to the domain connection screen.
When prompted, enter the e-mail address that you want to use for all e-mail messages sent from this domain. Then, click Next.
If you do not see any domain settings, you may not have permission to view this part of the HubSpot portal. To correct this situation, contact your Super Admin, who should grant you the necessary permissions.
Now that you have created the DKIM signature, you can connect it to your DNS record. You can log in to the domain name resolution service provider backend to find DNS resolution. You can then find the parsing management entry corresponding to the related domain.
Click add DNS record. Next, select the TXT tab. You can now enter all the information provided by HubSpot to verify your sending domain.
Monitor your email authentication health
Your email authentication will run most of the time in the background without any routine maintenance. However, authentication may mean that your latest activity produces a very high click-through rate (CTR) or ends up being spam.
Because the risk is so high, it is wise to monitor the health of your email authentication. This means paying close attention to your marketing indicators.
A surge in bounce rate or a sudden drop in participation may indicate a problem with your email authentication implementation. Fortunately, all of the email marketing platforms we introduced in this article have built-in analysis capabilities.
If you are using Mailchimp, you can view details about the latest e-mail activity. First, select the “Campaigns” icon.

Select the “Campaigns” button in Mailchimp
Then, find the email you want to check and select the View Report button that came with it. Mailchimp will now display all information about this activity, including bounce rate and open rate.

Click the “View Report” button in Mailchimp
If you use continuous contact, your dashboard will provide a dedicated reports tab. Here, you can view the analysis for a specific period.
This allows you to check whether your activity has experienced a sudden change in participation or a worrying surge in bounce rates. If you find a problem, you can find out exactly when the problem occurred by exploring different date ranges.
If you are a fan of HubSpot, you can view performance metrics from any email by logging into the HubSpot dashboard. Here, navigate to Marketing & gt; Email.

Navigate to Marketing and send an email in HubSpot
Select the email you want to check on the subsequent screen, and then select See details. This opens the Performance tab, where you can get a high-level overview of this email participation.
Summary
Email marketing is a great way to build brand awareness and push your contacts further into the sales channel. However, if you do not perform e-mail authentication, your well-designed marketing campaign may fall into the recipient’s spam folder.
Let’s take a quick look at the five main email authentication methods:
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): this method adds an encrypted signature to the title of the marketing message.
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): a technical standard that enables you to publish DNS records for all domains used to send marketing emails.
- Sender ID: supported by Microsoft, only a few select technologies use this standard to detect spoofing.
- Domain message authentication report and consistency (DMARC): this tells the server how to respond when it receives a message claiming to be from your domain but not authenticated by SPF or DKIM.
- Brand indicator for message recognition (BIMI): this unique method adds your logo to the authenticated message in the recipient’s inbox.

