Digital images are an inherent part of the network, and it is difficult to create any content without media. Inconspicuous still images are a great way to provide extra background for your writing.
however, without optimization, the file size of the image can be large. Lossy and lossless compression is a common consideration because each can reduce the size of the image, although quality tradeoffs also need to be taken into account.
you almost always need to apply some compression to the image. This keeps the quality at the acceptable level you specify, while reducing the file size. Choosing the right compression level will depend on your ultimate goals and requirements.
in this article, we will study lossy and lossless compression. Throughout the process, we will discuss the process of image “shaping”, what compression is, and many other aspects of optimizing the image. Differences between
- lossy and lossless elements of
- digital images
- network image optimization working principle
- lossy compression advantages and disadvantages of
- lossless compression
- how to choose between lossy and lossless
- use online compression services to optimize your image
hides the difference between
when it comes to any digital image compression There are several different formats to choose from. Sometimes these have other names based on many factors. However, at the core level, you will find two types:
lossy compression: the goal here is to provide the image with the smallest possible file size. As a result, image quality is usually low in the priority list.
- lossless compression:you will still find that using this compression format can significantly reduce file size but images are not affected by artifacts and other problems.
- in most cases, your decision about which format to use boils down to your ultimate goal: do you want small files, or do you focus on maintaining quality?lossy compression permanently removes data from the image that it deems unnecessary. It uses many different techniques to do this, resulting in a smaller file size.
lossless compression also deletes the data, but it can restore the original data if needed. The goal is to maintain high quality while reducing file size.
has several ways to do this, but the results are usually the same. To find the right option for your needs, let’s take a step back and review the basics of image and compression. Like software and Web development,
, the element of
digital images, usually has a “stack” that takes images from the camera to the Web. The
image starts with the “raw” data (hence the name RAW). This is similar to application code: fragments, rows, and values are converted to backgrounds with colors, image placeholders, dynamic elements, and so on.
for images, RAW files present slightly different image representations based on camera manufacturers, editing software, color space algorithms, etc. From there, you edit the image and export it to one of many file formats (described in more detail later):
edits the sample
of the RAW file in Capture One to make up several different elements of the standard digital image:
file types: different types of
will provide the quality of the final image that may or may not suit you. The key is to choose the most appropriate file type for the application.
- resolution:you will often see this expressed as megapixels (MP), but you will also use pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). Higher resolutions provide higher quality, but they also increase the initial file size
- bit depth: theaspect determines the color information in the image. Low depth renders only a few colors, while high depth may render millions of colors at a time. Generally speaking, the higher the better.
- size:this is the physical space occupied by the image. For example, 1000 pixels x 500 pixels can define the total size of an image.
- color space:this is an algorithm for determining how colors are displayed. The settings for each color space are different, which usually depends on the photographer’s preference.
- these elements combine to provide a final image of different quality. For example, a large JPEG photo with high resolution and high depth will provide the highest quality and definition:high-quality images
, even large-size images that can display a variety of colors will look poor at low resolutions:
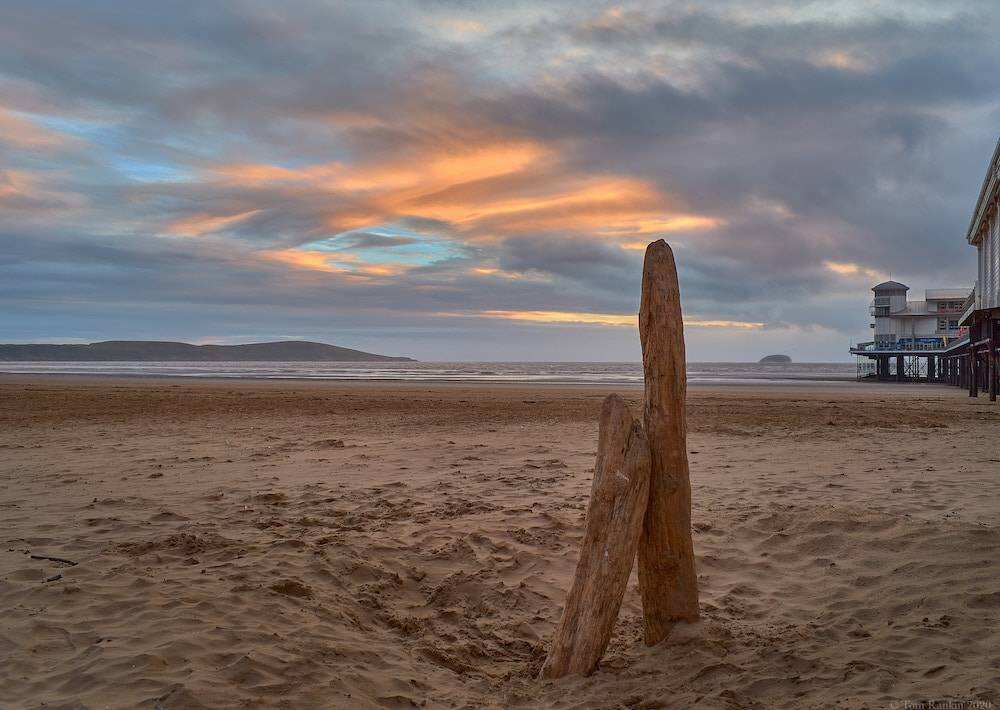

low-quality images
this balance is the way you develop core images before you apply compression. However, the format you use for the image has a significant impact on the final quality. How

Network Image Optimization works
because image compression is generally the same, you can apply standard rules to the way you optimize network images.
We have introduced many of these concepts elsewhere, but they are worth summarizing quickly for reference:
uses 72PPI resolution because it is the standard of the network. You can use a higher PPI/DPI for archiving reasons, but we assume you are publishing to the network.
sets the “long edge” of the image to 2048 pixels, because this is best for many different applications.
- use 8-bit color depth if you have a choice.
- runs images through compression and optimization tools prior to release.
- is a simple format that provides you with consistent results, although compression and optimization are what we will extend in the rest of this article.
- For this reason, let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of lossy compression and lossless compression. How
Image Compression helps your Web Image
in general, “compression” compresses the minimum and maximum values together. For example, compression increases the lowest volume in the music and lowers the highest volume. This makes the average level louder to the ear.
for images, compression is more like a restoration process. This means more emphasis on removing data from the image to reduce file size while maintaining the highest possible quality.
has many different proprietary algorithms that can help reduce the size of image files. In many cases, these are proprietary to a particular company. You will find many “lossy” and “lossless” compression standards, each with a unique descriptor:
, the compression option in
ShortPixel, to sum up, there are many benefits of applying image compression that are not unique to a particular format:
you can improve the performance of your site by keeping your file size small. By extending
, your site’s servers will have less work to do, affecting performance.
- small file size helps reduce server emissions. As a result, you help to contribute to a sustainable and ethical future.
- depending on your choice of algorithm and compression quality, you can display near-perfect and comparable quality.
- is just like creating shareable images, using various compression values, using a specific company, and choosing the right algorithm are critical to finding the right results for you. Advantages and disadvantages of
- lossy compression
lossy compression reduces the file size of the image and excludes almost all other aspects. The algorithm works by permanently deleting data. This can be as damaging as it sounds.
although we will not discuss the details too much, it is important to know that some data lossy compression deletions are visible in the image. The idea is to provide the best representation of raw, high-quality images in lighter weight-which means that some data will not be cut.
generally speaking, there are several benefits to using lossy compression:
ranks, they will get our weekly newsletter through WordPress insider tips! The
file size can be small– in some cases, less than 10KB. Despite the artifact of
, in many cases, the loss of quality is acceptable.
- this gives us the negative impact of using lossy compression-image quality decreases with any amount of compression:
- JPEG image compression slider
you will find that ribbons-color shadows are not rendered in the right way-and in some cases you will see a loss of edge sharpness. Images with fewer colors show less of this, but there is still a decrease in sharpness.
in addition, the deterioration of image quality is a permanent feature of the compression process. This means that the impact cannot be reversed in the future. Despite these shortcomings,
lossy compression is excellent for the performance of Web and your site. Small file sizes don’t always produce grainy images, although you can (of course) take things to the extreme: the example
of
overcompressed images, however, lossy is not the only option. Lossless compression is an alternative to quality-oriented website owners. Advantages and disadvantages of

Lossless Compression
Lossless Compression is just like what the label says: it compresses the file size of the image as much as possible without affecting the visible quality. It does this by deleting image metadata, which takes up unnecessary space: the
lossless compression algorithm for
images also looks for duplicate pixel sequences and encodes a shortcut to display them. For example, take the Command Line Interface as an example. You usually define its acronym once, and then use “CLI” (or the acronym of your choice) to refer to it at lightning speed in the same way that

lossless compression works because it is less destructive. While deleting metadata is irreversible, some compression will be reversible, making it a flexible algorithm for multiple uses. The advantage of
using lossless compression is to maintain quality: compared with all other algorithms,
lossless compression retains the highest quality in the image.
lossless is great for archiving purposes. For example, photographers can balance storage resources with images that retain the most data.
- lossless is the preferred compression algorithm for visual art: photography, graphic design, digital art and so on. It is almost possible to achieve “one-to-one” replication by combining lossless algorithm with appropriate depth and resolution.
- , however, there is one thing to note about the degree of service of lossless compression to specific areas: the scope of application is very small. This will reduce its overall availability.
- here are some other disadvantages of lossless compression to consider:
if the site uses many images, lossless compression may not be the best choice to display them. This is because in most cases, you will want to focus on smaller file sizes in these types of cases. Although
compression reduces the file size, the lossless algorithm does not change the image data as lossy. Because of this, you may only see a slight reduction in size, not an extreme slimming effect.
- next, we’ll look at the fastest (and possibly the best) way. How does
- choose between Lossy and Lossless
so you know the difference between lossy and lossless compression. However, you may still not know which algorithm is best to use on your site.
has two scenarios to consider:
can use lossy compression for most use cases on the network.
If you want to show photography or photography art, lossless compression will better serve you.
- these considerations depend on using one of the standard Web image formats, such as JPEG, PNG, or GIF. However, your compression requirements may vary depending on more modern formats such as HEIC and WebP.
- We will even say that unless you display photos on the site, lossy compression should be your default choice. WordPress compresses images by default, which shows that lossy compression is suitable for almost all applications.
uses online compression services to optimize your images
you can compress images in a number of ways before displaying them on your website. For example, you can choose to apply compression during the editing phase. In any case, this may be a by-product of conversion from RAW format.
, however, a popular choice is one of many online services. Each will provide a series of algorithms and exemplary user interfaces (UI). More importantly, most of them have some free services, at least try the application before you submit it.
We introduced some options in our article on image optimization, although these are WordPress-specific plug-ins that connect to the application programming interface (API). The good news is that many of these plug-ins also provide an online interface. For example, consider the ShortPixel:
ShortPixel interface
, where you drag images onto the uploader and wait for the application to compress and process them. However, you need to select the algorithm first, because the process will begin immediately. The choice of
is simple: two forms of lossy compression (“lossy” and “glossy”), and the lossless option. ShortPixel’s interface well explains the differences between each algorithm, and you can download images in a matter of seconds. Although both of
can meet your needs, the Imagify interface looks smoother and more professional than ShortPixel’s. There are also three “compression levels”– Normal, Aggressive, and Ultra:
Imagify interface
— the nuance here is that Imagify starts with lossless compression and then evolves into a lossy algorithm with severe artifacts. However, you will not find several other options in other solutions.

for beginners, you can keep the EXIF data of images intact and even resize them after conversion. This is sometimes priceless, especially if you want to apply compression levels that may delete EXIF data or limit the way images are resized.
is like its myth of the same name, Kraken can process your image and apply various types of compression. Most users will choose the lossy or lossless type.
Kraken interface
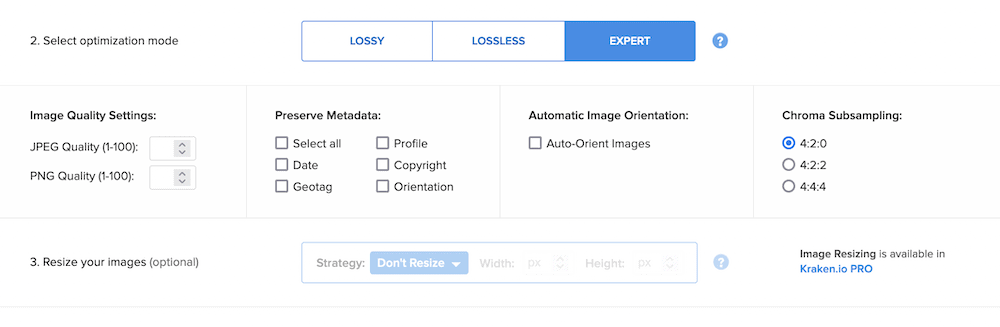
, however, there is also an expert mode: the
Kraken expert mode option
, which allows you to adjust compression and other options to suit your needs. For example, you can adjust the JPEG and PNG compression levels, choose to retain the metadata in the image, or even use chrominance subsampling to further change the color.
Summary
images look like a simple aspect of your site: you take a file, upload it to WordPress, and then add an image block to display it.
, however, there are a lot more things than you realize in the process of preparing images for the network. The compression format you choose will affect file size, image quality, and so on.
this article examines lossy and lossless compression and summarizes which one you should choose. Although walking a tightrope between quality and size, lossy compression is perfect for most use cases on the network. Photographers or those who are worried about tampering with image quality will want to use lossless compression, although there are fewer benefits in terms of file size.
但是,在为网络准备图像的过程中还有很多事情可能比您意识到的要多。您选择的压缩格式会影响文件大小、图像质量等。
这篇文章研究了有损与无损压缩,并总结了你应该选择哪一个。尽管在质量与大小之间走钢丝,但有损压缩对于网络上的大多数用例来说都是完美的。摄影师或那些担心篡改图像质量的人会希望使用无损压缩,尽管在文件大小方面的好处较少。

